Desmoplastic small round cell tumor of the lung: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 26744673
- PMCID: PMC4681984
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2015.08.010
Desmoplastic small round cell tumor of the lung: A case report and literature review
Abstract
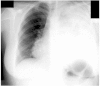
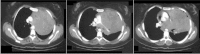
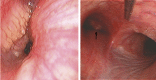
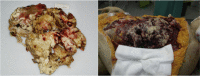
Desmoplastic small round cell tumor (DSRCT) is a rare, aggressive and malignant tumor that is characterized by nests of small tumor cells surrounded by a cellular and vascular collagenous stroma and predominantly affects young adolescent males. This tumor most commonly originates in the abdomen; however, in rare cases, DSRCT can originate in other body regions. The main manifestations of DSRCT are chest pain and respiratory symptoms, and patients' average survival after diagnosis is less than two years. In this report, we describe a case involving DSRCT of the lung that proved to be difficult to diagnose, and we conduct a literature review.
Keywords: Adenosine deaminase, ADA; Computed tomography, CT; Desmoplastic small round cell tumor; Desmoplastic small round cell tumor, DSRCT; Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA; Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/CT, FDG-PET/CT; Human immunodeficiency virus, HIV; Lactate dehydrogenase, LDH; Leukocyte common antigen, LCA; Lung cancer; Magnetic resonance imaging, MRI; Pleural effusion; Polymerase chain reaction, PCR; Primitive neuroectodermal tumor, PNET; Smooth muscle actin, SMA; Transbronchial needle aspiration, TBNA.
Figures
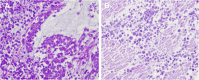
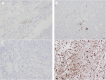
References
-
- Gerald W.L., Rosai J. Case 2. Desmoplastic small cell tumor with divergent differentiation. Pediatr. Pathol. 1989;9:177–183. - PubMed
-
- Argatoff L.H., O'Connell J.X., Mathers J.A., Gilks C.B., Sorensen P.H. Detection of the EWS/WT1 gene fusion by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of intra-abdominal desmoplastic small round cell tumor. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1996;20:406–412. - PubMed
-
- Sawyer J.R., Tryka A.F., Lewis J.M. A novel reciprocal chromosome translocation t(11;22)(p13;q12) in an intraabdominal desmoplastic small round-cell tumor. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1992;16:411–416. - PubMed
-
- Gerald W.L., Miller H.K., Battifora H., Miettinen M., Silva E.G., Rosai J. Intra-abdominal desmoplastic small round-cell tumor. Report of 19 cases of a distinctive type of high-grade polyphenotypic malignancy affecting young individuals. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1991;15:499–513. - PubMed
-
- Lal D.R., Su W.T., Wolden S.L., Loh K.C., Modak S., La Quaglia M.P. Results of multimodal treatment for desmoplastic small round cell tumors. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2005;40:251–255. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

