CCN1 (CYR61) and CCN3 (NOV) signaling drives human trophoblast cells into senescence and stimulates migration properties
- PMID: 26744771
- PMCID: PMC4853050
- DOI: 10.1080/19336918.2016.1139265
CCN1 (CYR61) and CCN3 (NOV) signaling drives human trophoblast cells into senescence and stimulates migration properties
Abstract
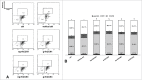
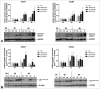
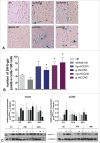
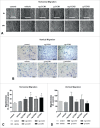
During placental development, continuous invasion of trophoblasts into the maternal compartment depends on the support of proliferating extravillous trophoblasts (EVTs). Unlike tumor cells, EVTs escape from the cell cycle before invasion into the decidua and spiral arteries. This study focused on the regulation properties of glycosylated and non-glycosylated matricellular CCN1 and CCN3, primarily for proliferation control in the benign SGHPL-5 trophoblast cell line, which originates from the first-trimester placenta. Treating SGHPL-5 trophoblast cells with the glycosylated forms of recombinant CCN1 and CCN3 decreased cell proliferation by bringing about G0/G1 cell cycle arrest, which was accompanied by the upregulation of activated Notch-1 and its target gene p21. Interestingly, both CCN proteins increased senescence-associated β-galactosidase activity and the expression of the senescence marker p16. The migration capability of SGHPL-5 cells was mostly enhanced in response to CCN1 and CCN3, by the activation of FAK and Akt kinase but not by the activation of ERK1/2. In summary, both CCN proteins play a key role in regulating trophoblast cell differentiation by inducing senescence and enhancing migration properties. Reduced levels of CCN1 and CCN3, as found in early-onset preeclampsia, could contribute to a shift from invasive to proliferative EVTs and may explain their shallow invasion properties in this disease.
Keywords: CCN1; CCN3; migration; placenta; senescence; trophoblast.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CCN3 Signaling Is Differently Regulated in Placental Diseases Preeclampsia and Abnormally Invasive Placenta.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Nov 16;11:597549. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.597549. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33304321 Free PMC article.
-
CCN3 regulates proliferation and migration properties in Jeg3 trophoblast cells via ERK1/2, Akt and Notch signalling.Mol Hum Reprod. 2013 Apr;19(4):237-49. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gas061. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Mol Hum Reprod. 2013. PMID: 23220688
-
Regulation of the matricellular proteins CYR61 (CCN1) and NOV (CCN3) by hypoxia-inducible factor-1{alpha} and transforming-growth factor-{beta}3 in the human trophoblast.Endocrinology. 2010 Jun;151(6):2835-45. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-1195. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20237132
-
Signalling pathways regulating the invasive differentiation of human trophoblasts: a review.Placenta. 2005 Apr;26 Suppl A:S21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2004.11.013. Placenta. 2005. PMID: 15837062 Review.
-
CCN proteins and cancer: two to tango.Front Biosci. 2005 May 1;10:998-1009. doi: 10.2741/1594. Front Biosci. 2005. PMID: 15769600 Review.
Cited by
-
Function of p21 (Cip1/Waf1/CDKN1A) in Migration and Invasion of Cancer and Trophoblastic Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jul 15;11(7):989. doi: 10.3390/cancers11070989. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31311187 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the Pathogenesis of Pre-eclampsia Using In Vitro Models of Spiral Uterine Artery Remodelling.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017 Oct 23;19(11):93. doi: 10.1007/s11906-017-0786-2. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017. PMID: 29063290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular communication network 1 promotes CASP2 mRNA expression but suppresses its protein translation in esophageal adenocarcinoma.J Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jul 17;18(3):e12046. doi: 10.1002/ccs3.12046. eCollection 2024 Sep. J Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39524140 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Gestational Arsenic Exposures on Placental and Fetal Development in Mice: The Role of Cyr61 .Environ Health Perspect. 2023 Sep;131(9):97004. doi: 10.1289/EHP12207. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Environ Health Perspect. 2023. PMID: 37682722 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Maternal Obesity in Mice on IL-6 Levels and Placental Endothelial Cell Homeostasis.Nutrients. 2020 Jan 22;12(2):296. doi: 10.3390/nu12020296. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 31979004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pijnenborg R, Dixon G, Robertson WB, Brosens I. Trophoblastic invasion of human decidua from 8 to 18 weeks of pregnancy. Placenta 1980; 1(1):3-19; PMID:7443635; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/S0143-4004(80)80012-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lyall F. Mechanisms regulating cytotrophoblast invasion in normal pregnancy and pre-eclampsia. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2006; 46(4):266-73; PMID:16866784; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1479-828X.2006.00589.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Handwerger S. New insights into the regulation of human cytotrophoblast cell differentiation. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2010; 323(1):94-104; PMID:20036312; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.mce.2009.12.015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ji L, Brkić J, Liu M, Fu G, Peng C, Wang YL. Placental trophoblast cell differentiation: physiological regulation and pathological relevance to preeclampsia. Mol Aspects Med 2013; 34(5):981-1023; PMID:23276825; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.mam.2012.12.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nakayama H, Scott IC, Cross JC. The transition to endoreduplication in trophoblast giant cells is regulated by the mSNA zinc finger transcription factor. Dev Biol 1998; 199(1):150-63; PMID:9676199; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1006/dbio.1998.8914 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
