Exploring the Role of Killer Cell Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors and Their HLA Class I Ligands in Autoimmune Hepatitis
- PMID: 26744892
- PMCID: PMC4712907
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146086
Exploring the Role of Killer Cell Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors and Their HLA Class I Ligands in Autoimmune Hepatitis
Abstract
Background: Natural killer cells are involved in the complex mechanisms underlying autoimmune diseases but few studies have investigated their role in autoimmune hepatitis. Killer immunoglobulin-like receptors are key regulators of natural killer cell-mediated immune responses.
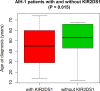
Methods and findings: KIR gene frequencies, KIR haplotypes, KIR ligands and combinations of KIRs and their HLA Class I ligands were investigated in 114 patients diagnosed with type 1 autoimmune hepatitis and compared with a group of 221 healthy controls. HLA Class I and Class II antigen frequencies were compared to those of 551 healthy unrelated families representative of the Sardinian population. In our cohort, type 1 autoimmune hepatitis was strongly associated with the HLA-B18, Cw5, DR3 haplotype. The KIR2DS1 activating KIR gene and the high affinity HLA-C2 ligands were significantly higher in patients compared to controls. Patients also had a reduced frequency of HLA-Bw4 ligands for KIR3DL1 and HLA-C1 ligands for KIR2DL3. Age at onset was significantly associated with the KIR2DS1 activating gene but not with HLA-C1 or HLA-C2 ligand groups.
Conclusions: The activating KIR gene KIR2DS1 resulted to have an important predictive potential for early onset of type 1 autoimmune hepatitis. Additionally, the low frequency of the KIR-ligand combinations KIR3DL1/HLA-Bw4 and KIR2DL3/HLA-C1 coupled to the high frequency of the HLA-C2 high affinity ligands for KIR2DS1 could contribute to unwanted NK cell autoreactivity in AIH-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
KIR and their HLA Class I ligands: Two more pieces towards completing the puzzle of chronic rejection and graft loss in kidney transplantation.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 7;12(7):e0180831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180831. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28686681 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphic HLA-C Receptors Balance the Functional Characteristics of KIR Haplotypes.J Immunol. 2015 Oct 1;195(7):3160-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501358. Epub 2015 Aug 26. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26311903 Free PMC article.
-
KIR gene mismatching and KIR/C ligands in liver transplantation: consequences for short-term liver allograft injury.Transplantation. 2013 Apr 27;95(8):1037-44. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318286486c. Transplantation. 2013. PMID: 23478359
-
KIR specificity and avidity of standard and unusual C1, C2, Bw4, Bw6 and A3/11 amino acid motifs at entire HLA:KIR interface between NK and target cells, the functional and evolutionary classification of HLA class I molecules.Int J Immunogenet. 2019 Aug;46(4):217-231. doi: 10.1111/iji.12433. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Int J Immunogenet. 2019. PMID: 31210416 Review.
-
The role genes encoding of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) and their ligands in susceptibility to and progression of HIV infection.Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2016 Dec 31;70(0):1409-1423. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1227771. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2016. PMID: 28100849 Review.
Cited by
-
NK Cell Subtypes as Regulators of Autoimmune Liver Disease.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016;2016:6903496. doi: 10.1155/2016/6903496. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016. PMID: 27462349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the Significance of HLA and KIR Diversity in Underrepresented Populations.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 15;12(6):1333. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061333. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Killer Ig-like Receptors in Diseases from A to Z.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 31;26(7):3242. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073242. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic Natural Killer Cells: Organ-Specific Sentinels of Liver Immune Homeostasis and Physiopathology.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 30;10:946. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00946. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31114585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of natural killer cells in liver inflammation.Semin Immunopathol. 2021 Aug;43(4):519-533. doi: 10.1007/s00281-021-00877-6. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Semin Immunopathol. 2021. PMID: 34230995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schramm C, Lohse AW. Autoimmune hepatitis on the rise. J Hepatol 2014;40:478–479. - PubMed
-
- Krawitt EL. Autoimmune hepatitis. N Engl J Med 2006;354:54–66. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez F, Berg PA, Bianchi FB, Bianchi L, Burroughs AK, Cancado EL, et al. Review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol 1999;3:929–938. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous