BAD, a Proapoptotic Protein, Escapes ERK/RSK Phosphorylation in Deguelin and siRNA-Treated HeLa Cells
- PMID: 26745145
- PMCID: PMC4706341
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145780
BAD, a Proapoptotic Protein, Escapes ERK/RSK Phosphorylation in Deguelin and siRNA-Treated HeLa Cells
Abstract
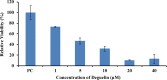
This study has been undertaken to explore the therapeutic effects of deguelin and specific siRNAs in HeLa cells. The data provided clearly show the silencing of ERK 1/2 with siRNAs and inhibition of ERK1/2 with deguelin treatment in HeLa cells. Additionally, we are providing information that deguelin binds directly to anti-apoptotic Bcl-2, Bcl-xl and Mcl-1 in the hydrophobic grooves, thereby releasing BAD and BAX from dimerization with these proteins. This results in increased apoptotic activity through the intrinsic pathway involved in rupture of mitochondrial membrane and release of cytochrome C. Evidence for inhibition of ERK1/2 by deguelin and escape of BAD phosphorylation at serine 112 through ERK/RSK pathway has been further fortified by obtaining similar results by silencing ERK 1/2 each with specific siRNAs. Increase in BAD after treatment with deguelin or siRNAs has been interpreted to mean that deguelin acts through several alternative pathways and therefore can be used as effective therapeutic agent.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterization of ERK docking domain inhibitors that induce apoptosis by targeting Rsk-1 and caspase-9.BMC Cancer. 2011 Jan 10;11:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-7. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21219631 Free PMC article.
-
Ursolic acid induces apoptosis through mitochondrial intrinsic pathway and suppression of ERK1/2 MAPK in HeLa cells.J Pharmacol Sci. 2014;125(2):202-10. doi: 10.1254/jphs.14017fp. Epub 2014 May 30. J Pharmacol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24881958
-
ERK-1 MAP kinase prevents TNF-induced apoptosis through bad phosphorylation and inhibition of Bax translocation in HeLa Cells.J Cell Biochem. 2009 Dec 1;108(5):1166-74. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22345. J Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19777442
-
Deguelin targets multiple oncogenic signaling pathways to combat human malignancies.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Apr;166:105487. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105487. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33581287 Review.
-
Pharmacological basis and new insights of deguelin concerning its anticancer effects.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Dec;174:105935. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105935. Epub 2021 Oct 10. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 34644595 Review.
Cited by
-
Caspase 3-specific cleavage of MEK1 suppresses ERK signaling and sensitizes cells to stress-induced apoptosis.FEBS Open Bio. 2023 Apr;13(4):684-700. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13574. Epub 2023 Feb 23. FEBS Open Bio. 2023. PMID: 36776127 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms and therapeutic potential.PeerJ. 2025 Jul 14;13:e19708. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19708. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40677749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potent Anti-Cancer Activity of 1-Dehydrodiosgenone from the Product of Microbial Transformation of Steroid Saponins.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 6;25(23):13118. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313118. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684828 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of G. applanatum Crude Polysaccharide Extract on Proinflammatory Cytokines and Proapoptotic Caspases in HeLa Cell Line: An In Vitro Study.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2023 Sep 19;2023:3593295. doi: 10.1155/2023/3593295. eCollection 2023. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 37767520 Free PMC article.
-
ERK1/2 and the Bcl-2 Family Proteins Mcl-1, tBid, and Bim Are Involved in Inhibition of Apoptosis During Persistent Chlamydia psittaci Infection.Inflammation. 2018 Aug;41(4):1372-1383. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0785-8. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29666982
References
-
- Chun K-H, Kosmeder JW, Sun S, Pezzuto JM, Lotan R, et al. (2003) Effects of deguelin on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway and apoptosis in premalignant human bronchial epithelial cells. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 95: 291–302. - PubMed
-
- Thamilselvan V, Menon M, Thamilselvan S (2011) Anticancer efficacy of deguelin in human prostate cancer cells targeting glycogen synthase kinase‐3 β/β‐catenin pathway. International Journal of Cancer 129: 2916–2927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

