Galectins are human milk glycan receptors
- PMID: 26747425
- PMCID: PMC4847615
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cww002
Galectins are human milk glycan receptors
Abstract
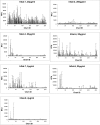
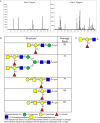
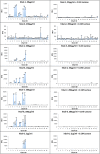
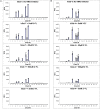
The biological recognition of human milk glycans (HMGs) is poorly understood. Because HMGs are rich in galactose we explored whether they might interact with human galectins, which bind galactose-containing glycans and are highly expressed in epithelial cells and other cell types. We screened a number of human galectins for their binding to HMGs on a shotgun glycan microarray consisting of 247 HMGs derived from human milk, as well as to a defined HMG microarray. Recombinant human galectins (hGal)-1, -3, -4, -7, -8 and -9 bound selectively to glycans, with each galectin recognizing a relatively unique binding motif; by contrast hGal-2 did not recognize HMGs, but did bind to the human blood group A Type 2 determinants on other microarrays. Unlike other galectins, hGal-7 preferentially bound to glycans expressing a terminal Type 1 (Galβ1-3GlcNAc) sequence, a motif that had eluded detection on non-HMG glycan microarrays. Interactions with HMGs were confirmed in a solution setting by isothermal titration microcalorimetry and hapten inhibition experiments. These results demonstrate that galectins selectively bind to HMGs and suggest the possibility that galectin-HMG interactions may play a role in infant immunity.
Keywords: galectins; glycan microarrays; glycan recognition; human milk glycans; shotgun glycomics.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional glycomic analysis of human milk glycans reveals the presence of virus receptors and embryonic stem cell biomarkers.J Biol Chem. 2012 Dec 28;287(53):44784-99. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.425819. Epub 2012 Oct 31. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23115247 Free PMC article.
-
Human milk contains novel glycans that are potential decoy receptors for neonatal rotaviruses.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014 Nov;13(11):2944-60. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.039875. Epub 2014 Jul 21. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 25048705 Free PMC article.
-
Human DC-SIGN binds specific human milk glycans.Biochem J. 2016 May 15;473(10):1343-53. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160046. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 26976925 Free PMC article.
-
Application of microarrays for deciphering the structure and function of the human glycome.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Apr;12(4):902-12. doi: 10.1074/mcp.R112.027110. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23412570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key regulators of galectin-glycan interactions.Proteomics. 2016 Dec;16(24):3111-3125. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201600116. Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27582340 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quantifying Biomolecular Interactions Using Slow Mixing Mode (SLOMO) Nanoflow ESI-MS.ACS Cent Sci. 2022 Jul 27;8(7):963-974. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.2c00215. Epub 2022 Jul 6. ACS Cent Sci. 2022. PMID: 35912341 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of Human Milk Oligosaccharides and Effects on Early Life Immune Development.Front Pediatr. 2018 Sep 10;6:239. doi: 10.3389/fped.2018.00239. eCollection 2018. Front Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 30250836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of the Clinical Experiences of Feeding Infants Formula Containing the Human Milk Oligosaccharide 2'-Fucosyllactose.Nutrients. 2018 Sep 21;10(10):1346. doi: 10.3390/nu10101346. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30241407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galectin-3 Decreases 4-1BBL Bioactivity by Crosslinking Soluble and Membrane Expressed 4-1BB.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 24;13:915890. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.915890. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35812455 Free PMC article.
-
Human milk oligosaccharides regulate human macrophage polarization and activation in response to Staphylococcus aureus.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 6;15:1379042. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1379042. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38903508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad N, Gabius HJ, Kaltner H, Andre S, Kuwabara I, Liu FT, Oscarson S, Norberg T, Brewer CF. 2002. Thermodynamic binding studies of cell surface carbohydrate epitopes to galectins-1,-3, and-7: Evidence for differential binding specificities. Can J Chem. 80:1096–1104.
-
- Bachhawat-Sikder K, Thomas CJ, Surolia A. 2001. Thermodynamic analysis of the binding of galactose and poly-N-acetyllactosamine derivatives to human galectin-3. FEBS Lett. 500:75–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

