Facile and cost-effective production of microscale PDMS architectures using a combined micromilling-replica moulding (μMi-REM) technique
- PMID: 26747434
- PMCID: PMC4706591
- DOI: 10.1007/s10544-015-0027-x
Facile and cost-effective production of microscale PDMS architectures using a combined micromilling-replica moulding (μMi-REM) technique
Abstract
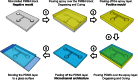
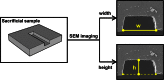
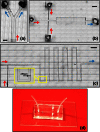
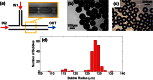
We describe a cost-effective and simple method to fabricate PDMS-based microfluidic devices by combining micromilling with replica moulding technology. It relies on the following steps: (i) microchannels are milled in a block of acrylic; (ii) low-cost epoxy adhesive resin is poured over the milled acrylic block and allowed to cure; (iii) the solidified resin layer is peeled off the acrylic block and used as a mould for transferring the microchannel architecture onto a PDMS layer; finally (iv) the PDMS layer is plasma bonded to a glass surface. With this method, microscale architectures can be fabricated without the need for advanced technological equipment or laborious and time-consuming intermediate procedures. In this manuscript, we describe and validate the microfabrication procedure, and we illustrate its applicability to emulsion and microbubble production.
Keywords: Emulsions; Microbubbles; Microchannel; Microfabrication; Microfluidic; Micromilling; Pdms; Pmma; Replica moulding.
Figures

References
-
- Becker H, Heim U. Hot embossing as a method for the fabrication of polymer high aspect ratio structures. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2000;83(1):130–135. doi: 10.1016/S0924-4247(00)00296-X. - DOI
-
- Borenstein JT, Terai H, et al. Microfabrication technology for vascularized tissue engineering. Biomed. Microdevices. 2002;4(3):167–175. doi: 10.1023/A:1016040212127. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

