Quality-of-life and performance status results from the phase III RAINBOW study of ramucirumab plus paclitaxel versus placebo plus paclitaxel in patients with previously treated gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 26747859
- PMCID: PMC4803452
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdv625
Quality-of-life and performance status results from the phase III RAINBOW study of ramucirumab plus paclitaxel versus placebo plus paclitaxel in patients with previously treated gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: The phase III RAINBOW trial demonstrated that the addition of ramucirumab to paclitaxel improved overall survival, progression-free survival, and tumor response rate in fluoropyrimidine-platinum previously treated patients with advanced gastric/gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma. Here, we present results from quality-of-life (QoL) and performance status (PS) analyses.
Patients and methods: Patients with Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group PS of 0/1 were randomized to receive ramucirumab (8 mg/kg i.v.) or placebo on days 1 and 15 of a 4-week cycle, with both arms receiving paclitaxel (80 mg/m(2)) on days 1, 8, and 15. Patient-reported outcomes were assessed with the QoL/health status questionnaires EORTC QLQ-C30 and EQ-5D at baseline and 6-week intervals. PS was assessed at baseline and day 1 of every cycle. Time to deterioration (TtD) in each QLQ-C30 scale was defined as randomization to first worsening of ≥10 points (on 100-point scale) and TtD in PS was defined as first worsening to ≥2. Hazard ratios (HRs) for treatment effect were estimated using stratified Cox proportional hazards models.
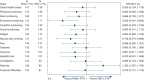
Results: Of the 665 patients randomized, 650 (98%) provided baseline QLQ-C30 and EQ-5D data, and 560 (84%) also provided data from ≥1 postbaseline time point. Baseline scores for both instruments were similar between arms. Of the 15 QLQ-C30 scales, 14 had HR < 1, indicating similar or longer TtD in QoL for ramucirumab + paclitaxel. Treatment with ramucirumab + paclitaxel was also associated with a delay in TtD in PS to ≥2 (HR = 0.798, P = 0.0941). Alternate definitions of PS deterioration yielded similar results: PS ≥ 3 (HR = 0.656, P = 0.0508), deterioration by ≥1 PS level (HR = 0.802, P = 0.0444), and deterioration by ≥2 PS levels (HR = 0.608, P = 0.0063). EQ-5D scores were comparable between treatment arms, stable during treatment, and worsened at discontinuation.
Conclusion: In patients with previously treated advanced gastric/GEJ adenocarcinoma, addition of ramucirumab to paclitaxel prolonged overall survival while maintaining patient QoL with delayed symptom worsening and functional status deterioration.
Clinicaltrialsgov: NCT01170663.
Keywords: EORTC QLQ-C30; EQ-5D; GEJ cancer; gastric cancer; quality of life; ramucirumab.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Figures

References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M et al. . GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11 [Internet]. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2013. http://globocan.iarc.fr, accessed on 16 May 2015.
-
- Price TJ, Shapiro JD, Segelov E et al. . Management of advanced gastric cancer. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 6: 199–209. - PubMed
-
- Thuss-Patience PC, Kretzschmar A, Bichev D et al. . Survival advantage for irinotecan versus best supportive care as second-line chemotherapy in gastric cancer—a randomised phase III study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie (AIO). Eur J Cancer 2011; 47: 2306–2314. - PubMed
-
- Kang JH, Lee SI, Lim DH et al. . Salvage chemotherapy for pretreated gastric cancer: a randomized phase III trial comparing chemotherapy plus best supportive care with best supportive care alone. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 1513–1518. - PubMed
-
- Ford HER, Marshall A, Bridgewater JA et al. . Docetaxel versus active symptom control for refractory oesophagogastric adenocarcinoma (COUGAR-02): an open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2014; 15: 78–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

