Regulation of antiviral innate immune signaling by stress-induced RNA granules
- PMID: 26748340
- PMCID: PMC4763080
- DOI: 10.1093/jb/mvv122
Regulation of antiviral innate immune signaling by stress-induced RNA granules
Abstract
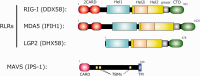
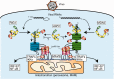
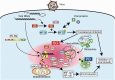
Activation of antiviral innate immunity is triggered by cellular pattern recognition receptors. Retinoic acid inducible gene-I (RIG-I)-like receptors (RLRs) detect viral non-self RNA in cytoplasm of virus-infected cells and play a critical role in the clearance of the invaded viruses through production of antiviral cytokines. Among the three known RLRs, RIG-I and melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 recognize distinct non-self signatures of viral RNA and activate antiviral signaling. Recent reports have clearly described the molecular machinery underlying the activation of RLRs and interactions with the downstream adaptor, mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS). RLRs and MAVS are thought to form large multimeric filaments around cytoplasmic organelles depending on the presence of Lys63-linked ubiquitin chains. Furthermore, RLRs have been shown to localize to stress-induced ribonucleoprotein aggregate known as stress granules and utilize them as a platform for recognition/activation of signaling. In this review, we will focus on the current understanding of RLR-mediated signal activation and the interactions with stress-induced RNA granules.
Keywords: RNA; innate immunity; retinoic acid inducible gene-I-like receptor; stress response; viral infection.
© The Authors 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Japanese Biochemical Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RNA recognition and signal transduction by RIG-I-like receptors.Immunol Rev. 2009 Jan;227(1):54-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00727.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19120475 Review.
-
Orchestrating the interferon antiviral response through the mitochondrial antiviral signaling (MAVS) adapter.Curr Opin Immunol. 2011 Oct;23(5):564-72. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2011.08.001. Epub 2011 Aug 22. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21865020 Review.
-
RIGorous detection: exposing virus through RNA sensing.Science. 2010 Jan 15;327(5963):284-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1185068. Science. 2010. PMID: 20075242
-
Regulation of RLR-mediated innate immune signaling--it is all about keeping the balance.Eur J Cell Biol. 2012 Jan;91(1):36-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2011.01.011. Epub 2011 Apr 9. Eur J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 21481967 Review.
-
Innate immunity to virus infection.Immunol Rev. 2009 Jan;227(1):75-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00737.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19120477 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus Activates Integrated Stress Response Pathway and Induces Stress Granules to Regulate Virus Replication.Viruses. 2023 Feb 7;15(2):466. doi: 10.3390/v15020466. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851680 Free PMC article.
-
How Many Mammalian Reovirus Proteins are involved in the Control of the Interferon Response?Pathogens. 2019 Jun 21;8(2):83. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8020083. Pathogens. 2019. PMID: 31234302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CpG and UpA dinucleotides in both coding and non-coding regions of echovirus 7 inhibit replication initiation post-entry.Elife. 2017 Sep 29;6:e29112. doi: 10.7554/eLife.29112. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28960178 Free PMC article.
-
Stress Granules in Infectious Disease: Cellular Principles and Dynamic Roles in Immunity and Organelles.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 2;25(23):12950. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312950. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress Granule Formation Attenuates RACK1-Mediated Apoptotic Cell Death Induced by Morusin.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 28;21(15):5360. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155360. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32731602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yoneyama M., Fujita T. (2010) Recognition of viral nucleic acids in innate immunity. Rev. Med. Virol. 20, 4–22 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

