Genotype Imputation with Millions of Reference Samples
- PMID: 26748515
- PMCID: PMC4716681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.11.020
Genotype Imputation with Millions of Reference Samples
Abstract
We present a genotype imputation method that scales to millions of reference samples. The imputation method, based on the Li and Stephens model and implemented in Beagle v.4.1, is parallelized and memory efficient, making it well suited to multi-core computer processors. It achieves fast, accurate, and memory-efficient genotype imputation by restricting the probability model to markers that are genotyped in the target samples and by performing linear interpolation to impute ungenotyped variants. We compare Beagle v.4.1 with Impute2 and Minimac3 by using 1000 Genomes Project data, UK10K Project data, and simulated data. All three methods have similar accuracy but different memory requirements and different computation times. When imputing 10 Mb of sequence data from 50,000 reference samples, Beagle's throughput was more than 100× greater than Impute2's throughput on our computer servers. When imputing 10 Mb of sequence data from 200,000 reference samples in VCF format, Minimac3 consumed 26× more memory per computational thread and 15× more CPU time than Beagle. We demonstrate that Beagle v.4.1 scales to much larger reference panels by performing imputation from a simulated reference panel having 5 million samples and a mean marker density of one marker per four base pairs.
Copyright © 2016 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


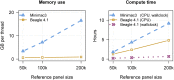
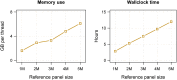
References
-
- Marchini J., Howie B. Genotype imputation for genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010;11:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Marchini J., Howie B., Myers S., McVean G., Donnelly P. A new multipoint method for genome-wide association studies by imputation of genotypes. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:906–913. - PubMed
-
- Wood A.R., Esko T., Yang J., Vedantam S., Pers T.H., Gustafsson S., Chu A.Y., Estrada K., Luan J., Kutalik Z., Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) Consortium. MIGen Consortium. PAGE Consortium. LifeLines Cohort Study Defining the role of common variation in the genomic and biological architecture of adult human height. Nat. Genet. 2014;46:1173–1186. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Speliotes E.K., Willer C.J., Berndt S.I., Monda K.L., Thorleifsson G., Jackson A.U., Lango Allen H., Lindgren C.M., Luan J., Mägi R., MAGIC. Procardis Consortium Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index. Nat. Genet. 2010;42:937–948. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

