Model-free Estimation of Recent Genetic Relatedness
- PMID: 26748516
- PMCID: PMC4716688
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.11.022
Model-free Estimation of Recent Genetic Relatedness
Abstract
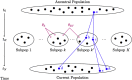
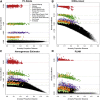
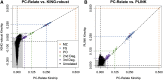
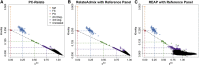
Genealogical inference from genetic data is essential for a variety of applications in human genetics. In genome-wide and sequencing association studies, for example, accurate inference on both recent genetic relatedness, such as family structure, and more distant genetic relatedness, such as population structure, is necessary for protection against spurious associations. Distinguishing familial relatedness from population structure with genotype data, however, is difficult because both manifest as genetic similarity through the sharing of alleles. Existing approaches for inference on recent genetic relatedness have limitations in the presence of population structure, where they either (1) make strong and simplifying assumptions about population structure, which are often untenable, or (2) require correct specification of and appropriate reference population panels for the ancestries in the sample, which might be unknown or not well defined. Here, we propose PC-Relate, a model-free approach for estimating commonly used measures of recent genetic relatedness, such as kinship coefficients and IBD sharing probabilities, in the presence of unspecified structure. PC-Relate uses principal components calculated from genome-screen data to partition genetic correlations among sampled individuals due to the sharing of recent ancestors and more distant common ancestry into two separate components, without requiring specification of the ancestral populations or reference population panels. In simulation studies with population structure, including admixture, we demonstrate that PC-Relate provides accurate estimates of genetic relatedness and improved relationship classification over widely used approaches. We further demonstrate the utility of PC-Relate in applications to three ancestrally diverse samples that vary in both size and genealogical complexity.
Copyright © 2016 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Ethnicity: Diversity is future for genetic analysis.Nature. 2016 Dec 14;540(7633):341. doi: 10.1038/540341d. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27974770 No abstract available.
References
-
- Price A.L., Patterson N.J., Plenge R.M., Weinblatt M.E., Shadick N.A., Reich D. Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 2006;38:904–909. - PubMed
-
- Thompson E.A. The estimation of pairwise relationships. Ann. Hum. Genet. 1975;39:173–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 DK085501/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM 099568/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085524/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085545/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM099568/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201100004C/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM075091/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 CA148958/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM 81062/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N02 HL064278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM 075091/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM 075091/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM031575/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085584/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM081062/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

