Suppressive Effect of Constructed shRNAs against Apollon Induces Apoptosis and Growth Inhibition in the HeLa Cell Line
- PMID: 26748613
- PMCID: PMC4949978
- DOI: 10.7508/ibj.2016.03.003
Suppressive Effect of Constructed shRNAs against Apollon Induces Apoptosis and Growth Inhibition in the HeLa Cell Line
Abstract
Background: Cervical cancer is the second most common female cancer worldwide. Inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) block apoptosis; therefore, therapeutic strategies targeting IAPs have attracted the interest of researchers in recent years. Apollon, a member of IAPs, inhibits apoptosis and cell death. RNA interference is a pathway in which small interfering RNA (siRNA) or shRNA (short hairpin RNA) inactivates the expression of target genes. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of constructed shRNAs on apoptosis and growth inhibition through the suppression of apollon mRNA in HeLa cell line.
Methods: Three shRNAs with binding ability to three different target sites of the first region of apollon gene were designed and cloned in pRNAin-H1.2/Neo vector. shRNA plasmids were then transfected in HeLa cells using electroporation. Down-regulation effects of apollon and the viability of HeLa cells were analyzed by RT-PCR, lactate dehydrogenase assay, and MTT assay, respectively. Also, the induction and morphological markers of apoptosis were evaluated by caspase assay and immunocytochemistry method.
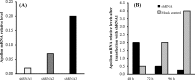
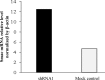
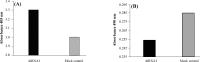
Results: The expression of shRNA in HeLa cells caused a significant decrease in the level of apollon mRNA1. In addition, shRNA1 effectively increased the mRNA level of Smac (as the antagonist of apollon), reduced the viability of HeLa cells and exhibited immunocytochemical apoptotic markers in this cell line.
Conclusion: Apollon gene silencing can induce apoptosis and growth impairment in HeLa cells. In this regard, apollon can be considered a candidate therapeutic target in HeLa cells as a positive human papillomavirus cancer cell line.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; Genetic association study; Iran; Single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Figures

References
-
- Karimi Zarchi M, Behtash N, Chiti Z, Kargar S. Cervical cancer and HPV vaccines in developing countries. Asian pacific journal of cancer prevention. 2009;10(6):969–974. - PubMed
-
- Green KL, Brown C, Roeder GE, Southgate TD, Gasto K. A cancer cell-specific inducer of apoptosis. Human gene therapy. 2007;18(6):547–561. - PubMed
-
- Fulda S, Debatin KM. Targeting inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) for diagnosis and treatment of human diseases. Recent patents on anti-cancer drug discovery. 2006;1(1):81–89. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
