Assessing cost-utility of predictive biomarkers in oncology: a streamlined approach
- PMID: 26749360
- PMCID: PMC5990969
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-016-3677-3
Assessing cost-utility of predictive biomarkers in oncology: a streamlined approach
Abstract
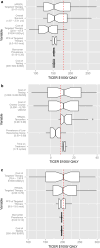
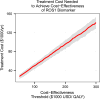
Evaluation of cost-utility is critical in assessing the medical utility of predictive or prognostic biomarkers. Current methods involve complex state-transition models, requiring comprehensive data inputs. We propose a simplified decision-analytic tool to explore the relative effect of factors contributing to the cost-utility of a biomarker. We derived a cost-utility metric, the "test incremental cost-effectiveness ratio" (TICER) for biomarker-guided treatment compared to no biomarker use. This method uses data inputs readily accessible through clinical literature. We compared our results with traditional cost-effectiveness analysis of predictive biomarkers for established (HER2-guided trastuzumab, ALK-guided crizotinib, OncotypeDX-guided adjuvant chemotherapy) and emerging (ROS1-guided crizotinib) targeted treatments. We conducted sensitivity analysis to determine which factors had the greatest impact on TICER estimates. Base case TICER for HER2 was $149,600/quality-adjusted life year (QALY), for ALK was $22,200/QALY, and for OncotypeDX was $11,600/QALY, consistent with literature-reported estimates ($180,000/QALY, $202,800/QALY, $8900/QALY, respectively). Base case TICER for ROS1-guided crizotinib was $205,900/QALY. Generally, when treatment cost is considerably greater than biomarker testing costs, TICER is driven by clinical outcomes and health-related quality of life, while biomarker prevalence and treatment cost have a lesser effect. Our simplified decision-analytic approach produces values consistent with existing cost-effectiveness analyses. Our results suggest that biomarker value is mostly driven by the clinical efficacy of the targeted agent. A user-friendly web tool for complete TICER analysis has been made available for open use at http://medicine.yale.edu/lab/pusztai/ticer/ .
Keywords: Breast cancer; Comparative effectiveness; Decision analysis; OncotypeDX; Outcomes; Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Fund C. Why not the best?: results from the National Scorecard on US Health System Performance 2008. Common-wealth Fund; New York: 2008.
-
- Woolf SH, Aron L. U.S. Health in International perspective: shorter lives, poorer health. In: Woolf SH, Aron L, editors. The National academies collection: reports funded by National Institutes of Health. Institute of Medicine of the National Academies; Washington: 2013. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, Fleming T, Eiermann W, Wolter J, Pegram M, Baselga J, Norton L. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(11):783–792. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200103153441101. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Herbst RS, Soria JC, Kowanetz M, Fine GD, Hamid O, Gordon MS, Sosman JA, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Gettinger SN, Kohrt HE, Horn L, Lawrence DP, Rost S, Leabman M, Xiao Y, Mokatrin A, Koeppen H, Hegde PS, Mellman I, Chen DS, Hodi FS. Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature. 2014;515(7528):563–567. doi: 10.1038/nature14011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

