Heterologous Immunity between Adenoviruses and Hepatitis C Virus: A New Paradigm in HCV Immunity and Vaccines
- PMID: 26751211
- PMCID: PMC4709057
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146404
Heterologous Immunity between Adenoviruses and Hepatitis C Virus: A New Paradigm in HCV Immunity and Vaccines
Abstract
Adenoviruses (Ad) are commonly used as vectors for gene therapy and/or vaccine delivery. Recombinant Ad vectors are being tested as vaccines for many pathogens. We have made a surprising observation that peptides derived from various hepatitis C virus (HCV) antigens contain extensive regions of homology with multiple adenovirus proteins, and conclusively demonstrate that adenovirus vector can induce robust, heterologous cellular and humoral immune responses against multiple HCV antigens. Intriguingly, the induction of this cross-reactive immunity leads to significant reduction of viral loads in a recombinant vaccinia-HCV virus infected mouse model, supporting their role in antiviral immunity against HCV. Healthy human subjects with Ad-specific pre-existing immunity demonstrated cross-reactive cellular and humoral immune responses against multiple HCV antigens. These findings reveal the potential of a previously uncharacterized property of natural human adenovirus infection to dictate, modulate and/or alter the course of HCV infection upon exposure. This intrinsic property of adenovirus vectors to cross-prime HCV immunity can also be exploited to develop a prophylactic and/or therapeutic vaccine against HCV.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
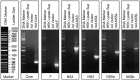

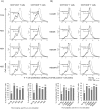



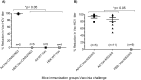

Similar articles
-
Heterologous Immunity between Adenoviruses and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV): Recombinant Adenovirus Vaccine Vectors Containing Antigens from Unrelated Pathogens Induce Cross-Reactive Immunity Against HCV Antigens.Cells. 2019 May 26;8(5):507. doi: 10.3390/cells8050507. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31130710 Free PMC article.
-
Unsolved Puzzles Surrounding HCV Immunity: Heterologous Immunity Adds Another Dimension.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 27;18(8):1626. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081626. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28749434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant adenoviral vector expressing HCV NS4 induces protective immune responses in a mouse model of Vaccinia-HCV virus infection: a dose and route conundrum.Vaccine. 2014 May 13;32(23):2712-21. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.02.080. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Vaccine. 2014. PMID: 24631092
-
Effect of route of delivery on heterologous protection against HCV induced by an adenovirus vector carrying HCV structural genes.Virol J. 2011 Nov 4;8:506. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-506. Virol J. 2011. PMID: 22054309 Free PMC article.
-
To Include or Occlude: Rational Engineering of HCV Vaccines for Humoral Immunity.Viruses. 2021 Apr 30;13(5):805. doi: 10.3390/v13050805. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33946211 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Respiratory virus-induced heterologous immunity: Part of the problem or part of the solution?Allergo J Int. 2018;27(3):79-96. doi: 10.1007/s40629-018-0056-0. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Allergo J Int. 2018. PMID: 32226720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Humoral immune response to adenovirus induce tolerogenic bystander dendritic cells that promote generation of regulatory T cells.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Aug 20;14(8):e1007127. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007127. eCollection 2018 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30125309 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous Immunity between Adenoviruses and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV): Recombinant Adenovirus Vaccine Vectors Containing Antigens from Unrelated Pathogens Induce Cross-Reactive Immunity Against HCV Antigens.Cells. 2019 May 26;8(5):507. doi: 10.3390/cells8050507. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31130710 Free PMC article.
-
Unsolved Puzzles Surrounding HCV Immunity: Heterologous Immunity Adds Another Dimension.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 27;18(8):1626. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081626. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28749434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterologous Immunity: Role in Natural and Vaccine-Induced Resistance to Infections.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 8;10:2631. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02631. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31781118 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McHutchison JG, Bacon BR. Chronic hepatitis C: an age wave of disease burden. Am J Manag Care. 2005;11(10 Suppl):S286–95; quiz S307-11. Epub 2005/10/20. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

