Mericitabine and Either Boceprevir or Telaprevir in Combination with Peginterferon Alfa-2a plus Ribavirin for Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Genotype 1 Infection and Prior Null Response: The Randomized DYNAMO 1 and DYNAMO 2 Studies
- PMID: 26752189
- PMCID: PMC4713467
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145409
Mericitabine and Either Boceprevir or Telaprevir in Combination with Peginterferon Alfa-2a plus Ribavirin for Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Genotype 1 Infection and Prior Null Response: The Randomized DYNAMO 1 and DYNAMO 2 Studies
Abstract
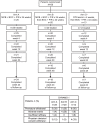
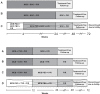
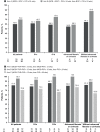
Most patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1 infection who have had a previous null response (<2-log10 reduction in HCV RNA by treatment week 12) to peginterferon/ribavirin (PegIFN/RBV) do not achieve a sustained virological response (SVR) when re-treated with a first-generation HCV protease inhibitor (PI) administered in combination with PegIFN/RBV. We studied the incremental benefits associated with adding mericitabine (nucleoside analog inhibitor of HCV polymerase) to PI plus PegIFN alfa-2a/RBV-based therapy in two double-blind randomized multicenter phase 2 trials (with boceprevir in DYNAMO 1, and with telaprevir in DYNAMO 2). The primary endpoint in both trials was SVR, defined as HCV RNA <25 IU/mL 12 weeks after the end of treatment (SVR12). Overall, the addition of mericitabine to PI plus PegIFN alfa-2a/RBV therapy resulted in SVR12 rates of 60-70% in DYNAMO 1 and of 71-96% in DYNAMO 2. SVR12 rates were similar in patients infected with HCV genotype 1a and 1b in both trials. The placebo control arms in both studies were stopped because of high rates of virological failure. Numerically lower relapse rates were associated with longer treatment with mericitabine (24 versus 12 weeks), telaprevir-containing regimens, and regimens that included 48 weeks of PegIFN alfa-2a/RBV therapy. No mericitabine resistance mutations were identified in any patient in either trial. The addition of mericitabine did not add to the safety burden associated with either telaprevir or boceprevir-based regimens. These studies demonstrate increased SVR rates and reduced relapse rates in difficult-to-treat patients when a nucleoside polymerase inhibitor with intermediate antiviral potency is added to regimens containing a first-generation PI.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01482403 and ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01482390.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Daclatasvir vs telaprevir plus peginterferon alfa/ribavirin for hepatitis C virus genotype 1.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Mar 28;22(12):3418-31. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i12.3418. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27022224 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Simeprevir versus telaprevir with peginterferon and ribavirin in previous null or partial responders with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection (ATTAIN): a randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority phase 3 trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2015 Jan;15(1):27-35. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(14)71002-3. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25482330 Clinical Trial.
-
PROPEL: a randomized trial of mericitabine plus peginterferon alpha-2a/ribavirin therapy in treatment-naïve HCV genotype 1/4 patients.Hepatology. 2013 Aug;58(2):524-37. doi: 10.1002/hep.26274. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23348636 Clinical Trial.
-
Telaprevir: a review of its use in the management of genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C.Drugs. 2012 Mar 26;72(5):619-41. doi: 10.2165/11208370-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22439668 Review.
-
Phase III results of Boceprevir in treatment naïve patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1.Liver Int. 2012 Feb;32 Suppl 1:27-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2011.02725.x. Liver Int. 2012. PMID: 22212568 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in the discovery of potent RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase (RdRp) inhibitors targeting viruses.RSC Med Chem. 2020 Dec 23;12(3):306-320. doi: 10.1039/d0md00318b. eCollection 2021 Mar 1. RSC Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 34046618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) inhibitors: The current landscape and repurposing for the COVID-19 pandemic.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Mar 5;213:113201. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113201. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33524687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-Heterocycles as Promising Antiviral Agents: A Comprehensive Overview.Molecules. 2024 May 10;29(10):2232. doi: 10.3390/molecules29102232. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38792094 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- AASLD/IDSA/IAS–USA. Recommendations for testing, managing, and treating hepatitis C. http://www.hcvguidelines.org [Accessed May 14, 2015]. Available from: http://www.hcvguidelines.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

