Transcriptome Analysis of Salt Stress Responsiveness in the Seedlings of Dongxiang Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.)
- PMID: 26752408
- PMCID: PMC4709063
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146242
Transcriptome Analysis of Salt Stress Responsiveness in the Seedlings of Dongxiang Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.)
Abstract
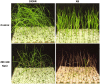
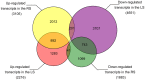
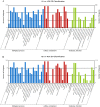
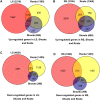
Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) is the progenitor of cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.), and is well known for its superior level of tolerance against cold, drought and diseases. To date, however, little is known about the salt-tolerant character of Dongxiang wild rice. To elucidate the molecular genetic mechanisms of salt-stress tolerance in Dongxiang wild rice, the Illumina HiSeq 2000 platform was used to analyze the transcriptome profiles of the leaves and roots at the seedling stage under salt stress compared with those under normal conditions. The analysis results for the sequencing data showed that 6,867 transcripts were differentially expressed in the leaves (2,216 up-regulated and 4,651 down-regulated) and 4,988 transcripts in the roots (3,105 up-regulated and 1,883 down-regulated). Among these differentially expressed genes, the detection of many transcription factor genes demonstrated that multiple regulatory pathways were involved in salt stress tolerance. In addition, the differentially expressed genes were compared with the previous RNA-Seq analysis of salt-stress responses in cultivated rice Nipponbare, indicating the possible specific molecular mechanisms of salt-stress responses for Dongxiang wild rice. A large number of the salt-inducible genes identified in this study were co-localized onto fine-mapped salt-tolerance-related quantitative trait loci, providing candidates for gene cloning and elucidation of molecular mechanisms responsible for salt-stress tolerance in rice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis of phosphorus stress responsiveness in the seedlings of Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.).Biol Res. 2018 Mar 15;51(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s40659-018-0155-x. Biol Res. 2018. PMID: 29544529 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of drought stress on global gene expression profile in leaf and root samples of Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon).Biosci Rep. 2017 Jun 27;37(3):BSR20160509. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160509. Print 2017 Jun 30. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28424372 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) to investigate lost/acquired genes during rice domestication.BMC Plant Biol. 2016 Apr 26;16:103. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0788-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 27118394 Free PMC article.
-
Advances and Challenges in the Breeding of Salt-Tolerant Rice.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 9;21(21):8385. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218385. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33182265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salt tolerance in rice: seedling and reproductive stage QTL mapping come of age.Theor Appl Genet. 2021 Nov;134(11):3495-3533. doi: 10.1007/s00122-021-03890-3. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Theor Appl Genet. 2021. PMID: 34287681 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis uncovers different heat stress responses in heat-resistant and heat-sensitive jujube cultivars.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 21;15(9):e0235763. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235763. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32956359 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Zinc Finger Transcription Factor ZAT6 Enhances Salt Tolerance.Open Life Sci. 2018 Nov 9;13:431-445. doi: 10.1515/biol-2018-0052. eCollection 2018 Jan. Open Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 33817112 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Molecular Mechanisms under Salt Stress in Leaves of Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.).Plants (Basel). 2022 Jul 18;11(14):1864. doi: 10.3390/plants11141864. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35890498 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Evaluation and Analysis of the Mechanism of Cold Tolerance Based on the Transcriptome of Weedy Rice Seedlings.Rice (N Y). 2020 Feb 13;13(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12284-019-0363-1. Rice (N Y). 2020. PMID: 32056019 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome profiling reveals the effects of drought tolerance in Giant Juncao.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Jan 4;21(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02785-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33390157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liang J, Qu Y, Yang C, Ma X, Cao G, Zhao Z, et al. Identification of QTLs associated with salt or alkaline tolerance at the seedling stage in rice under salt or alkaline stress. Euphytica 2015. February 01; 201(3): 441–52.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

