Transcriptome Profiling of Wild Arachis from Water-Limited Environments Uncovers Drought Tolerance Candidate Genes
- PMID: 26752807
- PMCID: PMC4695501
- DOI: 10.1007/s11105-015-0882-x
Transcriptome Profiling of Wild Arachis from Water-Limited Environments Uncovers Drought Tolerance Candidate Genes
Abstract
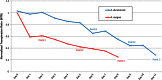
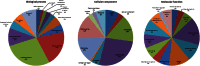
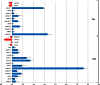
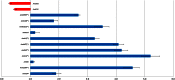
Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) is an important legume cultivated mostly in drought-prone areas where its productivity can be limited by water scarcity. The development of more drought-tolerant varieties is, therefore, a priority for peanut breeding programs worldwide. In contrast to cultivated peanut, wild relatives have a broader genetic diversity and constitute a rich source of resistance/tolerance alleles to biotic and abiotic stresses. The present study takes advantage of this diversity to identify drought-responsive genes by analyzing the expression profile of two wild species, Arachis duranensis and Arachis magna (AA and BB genomes, respectively), in response to progressive water deficit in soil. Data analysis from leaves and roots of A. duranensis (454 sequencing) and A. magna (suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH)) stressed and control complementary DNA (cDNA) libraries revealed several differentially expressed genes in silico, and 44 of them were selected for further validation by quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR). This allowed the identification of drought-responsive candidate genes, such as Expansin, Nitrilase, NAC, and bZIP transcription factors, displaying significant levels of differential expression during stress imposition in both species. This is the first report on identification of differentially expressed genes under drought stress and recovery in wild Arachis species. The generated transcriptome data, besides being a valuable resource for gene discovery, will allow the characterization of new alleles and development of molecular markers associated with drought responses in peanut. These together constitute important tools for the peanut breeding program and also contribute to a better comprehension of gene modulation in response to water deficit and rehydration.
Keywords: 454 Sequencing; Differential gene expression; Dry-down; Peanut wild relatives; SSH libraries; qRT-PCR.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Global transcriptome analysis of two wild relatives of peanut under drought and fungi infection.BMC Genomics. 2012 Aug 13;13:387. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-387. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22888963 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the treasure trove of drought-responsive genes in wild-type peanut through transcriptomics and physiological analyses of root.Funct Integr Genomics. 2022 Apr;22(2):215-233. doi: 10.1007/s10142-022-00833-z. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Funct Integr Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35195841
-
Early responses to dehydration in contrasting wild Arachis species.PLoS One. 2018 May 30;13(5):e0198191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198191. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29847587 Free PMC article.
-
The genus Arachis: an excellent resource for studies on differential gene expression for stress tolerance.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Oct 30;14:1275854. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1275854. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 38023864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in genetic engineering of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.)--a review.Plant Biotechnol J. 2015 Feb;13(2):147-62. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12339. Plant Biotechnol J. 2015. PMID: 25626474 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-Coding RNAs in Response to Drought Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 20;22(22):12519. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212519. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Old and young duplicate genes reveal different responses to environmental changes in Arachis duranensis.Mol Genet Genomics. 2019 Oct;294(5):1199-1209. doi: 10.1007/s00438-019-01574-8. Epub 2019 May 10. Mol Genet Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31076861
-
Introgression of wild alleles into the tetraploid peanut crop to improve water use efficiency, earliness and yield.PLoS One. 2018 Jun 11;13(6):e0198776. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198776. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29889864 Free PMC article.
-
Root Transcriptome Analysis of Wild Peanut Reveals Candidate Genes for Nematode Resistance.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 21;10(10):e0140937. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140937. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26488731 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of drought stress on global gene expression profile in leaf and root samples of Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon).Biosci Rep. 2017 Jun 27;37(3):BSR20160509. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160509. Print 2017 Jun 30. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28424372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertioli DJ, Seijo G, Freitas FO, Valls JFM, Leal-Bertioli SCM, Moretzsohn MC. An overview of peanut and its wild relatives. Plant Genet Resour. 2011;9:134–149. doi: 10.1017/S1479262110000444. - DOI
-
- Brasileiro ACM, Araujo ACG, Leal-Bertioli SC, Guimarães PM. Genomics and genetic transformation in Arachis. Int J Plant Biol Res. 2014;2:1017.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
