Autotransplantation
- PMID: 26752848
- PMCID: PMC4693328
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-0707.168827
Autotransplantation
Abstract
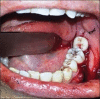
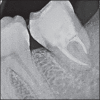
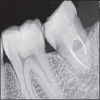
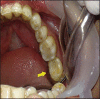
Autogenous tooth transplantation refers to the repositioning of autogenous teeth in another tooth extraction site or a surgically formed recipient site to replace missing teeth due to congenital deformity, grossly decayed carious teeth, mobile teeth due to periodontal disease, teeth lost due to trauma, endodontic failure or any other reason when a suitable donor tooth is available. This is a case report of autotransplantation of impacted #38 with complete root formation into the extraction site of grossly decayed, unrestorable #37 with 18 months follow-up showing excellent periapical healing and tooth stability. In autogenous tooth transplantation, even if the donor's tooth has complete root formation, a high success rate can be achieved if the cases are selected and treated properly. Chances of root resorption are there because of necrotic pulp and periodontal irritation during manipulation. However, autogenous tooth transplantation should always be considered as a good treatment modality in feasible cases.
Keywords: Autotransplantation; missing teeth; root resorption.
Figures


References
-
- Reich PP. Autogenous transplantation of maxillary and mandibular molars. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;66:2314–7. - PubMed
-
- Natiella JR, Armitage JE, Greene GW. The replantation and transplantation of teeth. A review. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1970;29:397–419. - PubMed
-
- Tsukiboshi M. Autogenous tooth transplantation: A reevaluation. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1993;13:120–49. - PubMed
-
- Ustad F, Ali FM, Kota Z, Mustafa A, Khan MI. Autotransplantation of teeth: A review. Am J Med Dent Sci. 2013;1:25–30.
-
- Unni KN, Singh VP. Autotransplantation of teeth: An overview. Amrita J Med. 2012;8:16–22.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

