Roles of cofactors and chromatin accessibility in Hox protein target specificity
- PMID: 26753000
- PMCID: PMC4705621
- DOI: 10.1186/s13072-015-0049-x
Roles of cofactors and chromatin accessibility in Hox protein target specificity
Abstract
Background: The regulation of specific target genes by transcription factors is central to our understanding of gene network control in developmental and physiological processes yet how target specificity is achieved is still poorly understood. This is well illustrated by the Hox family of transcription factors as their limited in vitro DNA-binding specificity contrasts with their clear in vivo functional specificity.
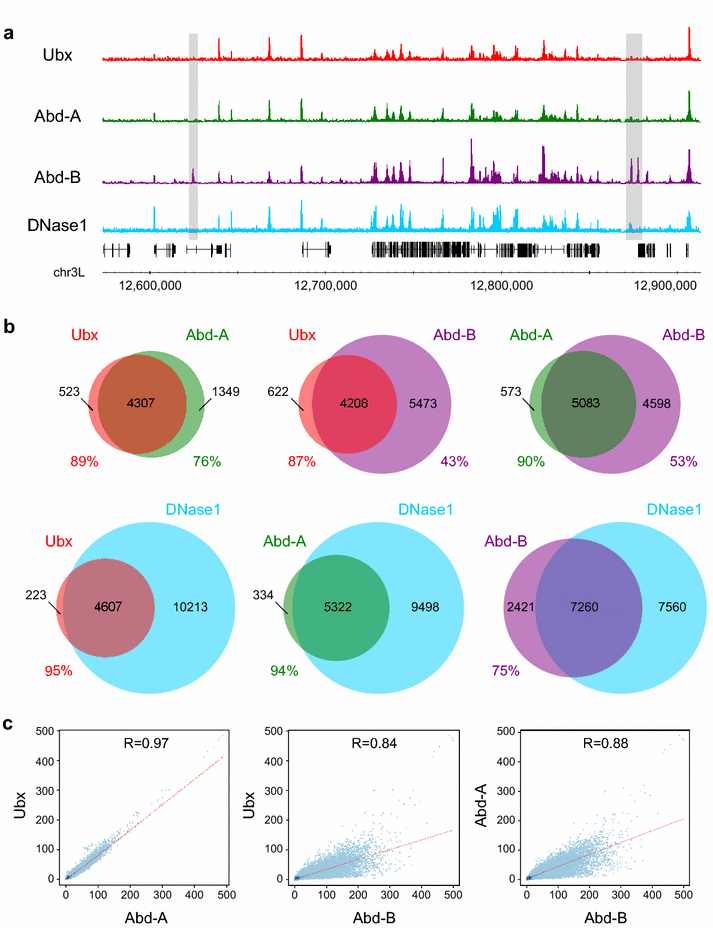
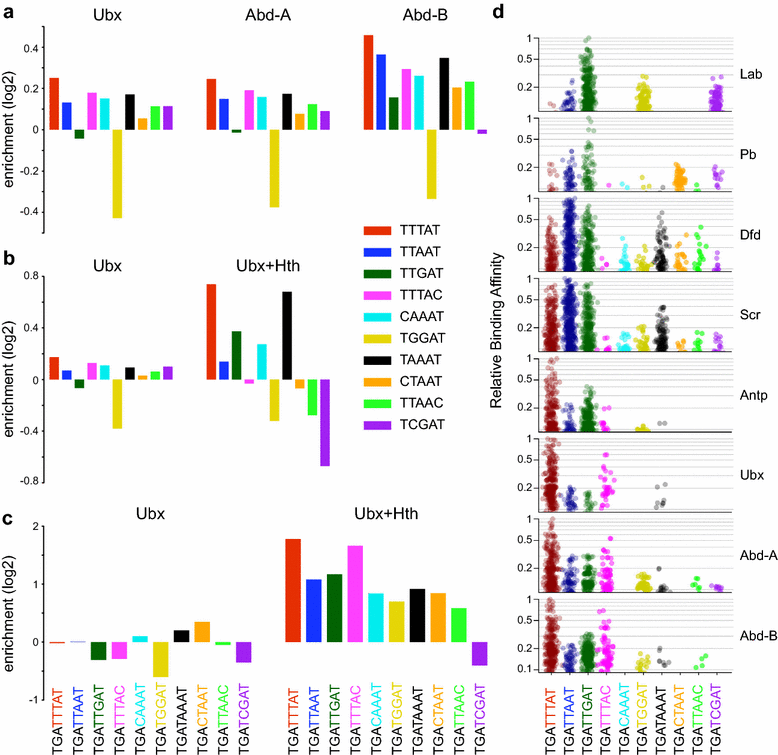
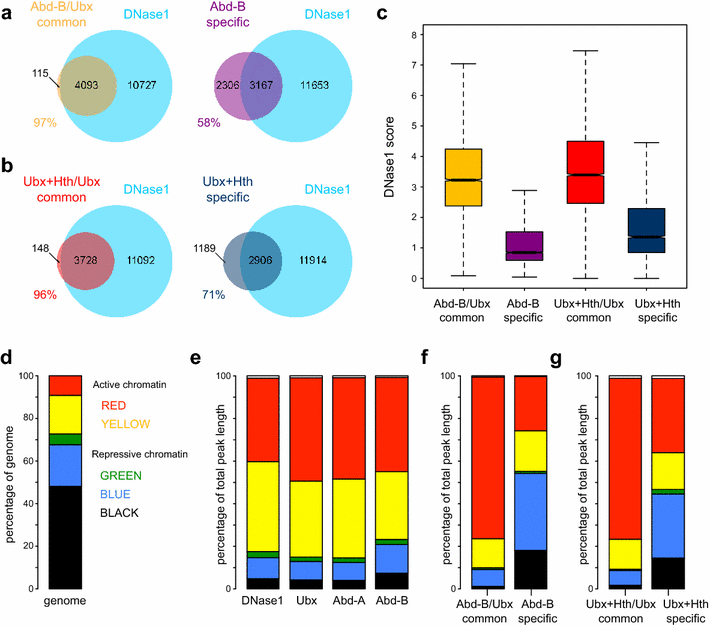
Results: We generated genome-wide binding profiles for three Hox proteins, Ubx, Abd-A and Abd-B, following transient expression in Drosophila Kc167 cells, revealing clear target specificity and a striking influence of chromatin accessibility. In the absence of the TALE class homeodomain cofactors Exd and Hth, Ubx and Abd-A bind at a very similar set of target sites in accessible chromatin, whereas Abd-B binds at an additional specific set of targets. Provision of Hox cofactors Exd and Hth considerably modifies the Ubx genome-wide binding profile enabling Ubx to bind at an additional novel set of targets. Both the Abd-B specific targets and the cofactor-dependent Ubx targets are in chromatin that is relatively DNase1 inaccessible prior to the expression of Hox proteins/Hox cofactors.
Conclusions: Our experiments demonstrate a strong role for chromatin accessibility in Hox protein binding and suggest that Hox protein competition with nucleosomes has a major role in Hox protein target specificity in vivo.
Keywords: Chromatin accessibility; Hox proteins; Transcription factor.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Chromatin accessibility plays a key role in selective targeting of Hox proteins.Genome Biol. 2019 Jun 3;20(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1721-4. Genome Biol. 2019. PMID: 31159833 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of the binding of the Hox protein Ultrabithorax and the Hox cofactor Homothorax in Drosophila.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 5;6(4):e14778. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014778. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21483667 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonism versus cooperativity with TALE cofactors at the base of the functional diversification of Hox protein function.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(2):e1003252. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003252. Epub 2013 Feb 7. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23408901 Free PMC article.
-
TALE transcription factors: Cofactors no more.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jan-Feb;152-153:76-84. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.11.015. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 36509674 Review.
-
Hox transcription factors and their elusive mammalian gene targets.Heredity (Edinb). 2006 Aug;97(2):88-96. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6800847. Epub 2006 May 24. Heredity (Edinb). 2006. PMID: 16721389 Review.
Cited by
-
The Hox transcription factor Ultrabithorax binds RNA and regulates co-transcriptional splicing through an interplay with RNA polymerase II.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jan 25;50(2):763-783. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1250. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 34931250 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms Underlying Hox-Mediated Transcriptional Outcomes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 16;9:787339. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.787339. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34869389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Drosophila Hox Genes in the Assembly of Neuromuscular Networks and Behavior.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 7;9:786993. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.786993. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35071230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A bioinformatics screen reveals hox and chromatin remodeling factors at the Drosophila histone locus.BMC Genom Data. 2023 Sep 21;24(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12863-023-01147-0. BMC Genom Data. 2023. PMID: 37735352 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin accessibility plays a key role in selective targeting of Hox proteins.Genome Biol. 2019 Jun 3;20(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1721-4. Genome Biol. 2019. PMID: 31159833 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

