Comparison of needle aspiration and vacuum-assisted biopsy in the ultrasound-guided drainage of lactational breast abscesses
- PMID: 26753603
- PMCID: PMC4825204
- DOI: 10.14366/usg.15041
Comparison of needle aspiration and vacuum-assisted biopsy in the ultrasound-guided drainage of lactational breast abscesses
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to compare needle aspiration and vacuum-assistedbiopsy in the ultrasound-guided treatment of lactational breast abscesses.
Methods: Between January 2005 and December 2014, a total of 74 patients presented withlactational breast abscesses. Thirty of these patients underwent treatment with antibioticsalone, while the remaining 44 lactating women with breast abscesses were treated withneedle aspiration (n=25) or vacuum-assisted biopsy (n=19). Age, duration of lactation, abscess diameter, pus culture results, the number of interventions, the healing time, and the cure rate were reviewed and compared between these two groups. The Student's t test and the chi-square test were used to compare the variables.
Results: No significant difference was found in the cure rate between the needle aspirationgroup (22/25, 88%) and the vacuum-assisted biopsy group (18/19, 94.7%) (P=0.441). However, the mean healing time was significantly shorter in the vacuum-assisted biopsy group (6.7 days) than in the needle aspiration group (9.0 days) (P=0.001).
Conclusion: Vacuum-assisted biopsy is a viable option for the management of lactational breast abscesses and was found to lead to a shorter healing time than needle aspiration. However, further study is necessary to establish the clinical efficacy of vacuum-assisted biopsy in the management of lactational breast abscesses.
Keywords: Abscess; Aspiration, vacuum-assisted; Biopsy, needle; Breast; Image-guided biopsy; Ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest to this article was reported.
Figures
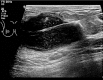
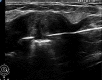
References
-
- Trop I, Dugas A, David J, El Khoury M, Boileau JF, Larouche N, et al. Breast abscesses: evidence-based algorithms for diagnosis, management, and follow-up. Radiographics. 2011;31:1683–1699. - PubMed
-
- Benson EA. Management of breast abscesses. World J Surg. 1989;13:753–756. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz RJ, Shrestha R. Needle aspiration of breast abscesses. Am J Surg. 2001;182:117–119. - PubMed
-
- Karstrup S, Solvig J, Nolsoe CP, Nilsson P, Khattar S, Loren I, et al. Acute puerperal breast abscesses: US-guided drainage. Radiology. 1993;188:807–809. - PubMed
-
- Eryilmaz R, Sahin M, Hakan Tekelioglu M, Daldal E. Management of lactational breast abscesses. Breast. 2005;14:375–379. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

