Increased cerebrospinal fluid soluble TREM2 concentration in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 26754172
- PMCID: PMC4709982
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-016-0071-x
Increased cerebrospinal fluid soluble TREM2 concentration in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
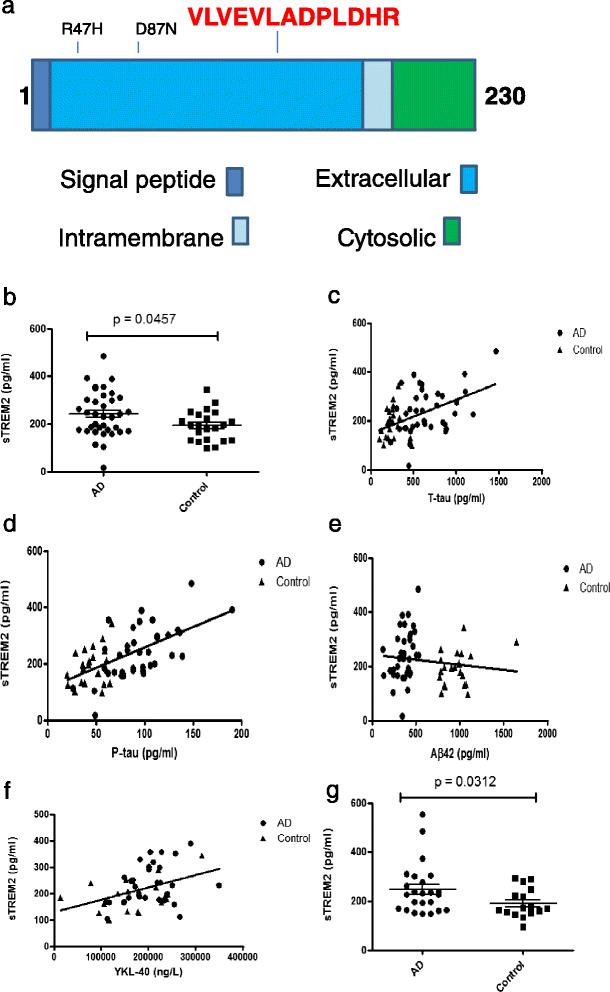
Background: The discovery that heterozygous missense mutations in the gene encoding triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) are risk factors for Alzheimer's disease (AD), with only the apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 gene allele conferring a higher risk, has led to increased interest in immune biology in the brain. TREM2 is expressed on microglia, the resident immune cells of the brain and has been linked to phagocytotic clearance of amyloid β (Aβ) plaques. Soluble TREM2 (sTREM2) has previously been measured in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) by ELISA but in our hands commercial kits have proved unreliable, suggesting that other methods may be required. We developed a mass spectrometry method using selected reaction monitoring for the presence of a TREM2 peptide, which can be used to quantify levels of sTREM2 in CSF.
Findings: We examined CSF samples from memory clinics in Sweden and the UK. For all samples the following were available: clinical diagnosis, age, sex, and measurements of the CSF AD biomarkers Aβ42, T-tau and P-tau181. AD patients (n = 37) all met biomarker (IWG2) criteria for AD. Control individuals (n = 22) were cognitively normal without evidence for AD in CSF. We found significantly higher sTREM2 concentration in AD compared to control CSF. There were significant correlations between CSF sTREM2 and T-tau as well as P-tau181. CSF sTREM2 increase in AD was replicated in a second, independent cohort consisting of 24 AD patients and 16 healthy volunteers.
Conclusion: CSF concentrations of sTREM2 are higher in AD than in controls, and correlate with markers of neurodegeneration. CSF sTREM2 may be used to quantify glial activation in AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early increase of CSF sTREM2 in Alzheimer's disease is associated with tau related-neurodegeneration but not with amyloid-β pathology.Mol Neurodegener. 2019 Jan 10;14(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0301-5. Mol Neurodegener. 2019. PMID: 30630532 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal fluid soluble TREM2 in aging and Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2016 Apr 27;8(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13195-016-0182-1. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27121148 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroimaging biomarkers and CSF sTREM2 levels in Alzheimer's disease: a longitudinal study.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 3;14(1):15318. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66211-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38961148 Free PMC article.
-
TREM2 ectodomain and its soluble form in Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jul 7;17(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01878-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32635934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous analysis of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers using microsphere-based xMAP multiplex technology for early detection of Alzheimer's disease.Methods. 2012 Apr;56(4):484-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.03.023. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Methods. 2012. PMID: 22503777 Review.
Cited by
-
The longitudinal trajectory of CSF sTREM2: the alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Jun 26;16(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01506-8. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38926894 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid beta, tau, synaptic, neurodegeneration, and glial biomarkers in the preclinical stage of the Alzheimer's continuum.Alzheimers Dement. 2020 Oct;16(10):1358-1371. doi: 10.1002/alz.12131. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Alzheimers Dement. 2020. PMID: 32573951 Free PMC article.
-
Higher CSF sTREM2 attenuates ApoE4-related risk for cognitive decline and neurodegeneration.Mol Neurodegener. 2020 Oct 8;15(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13024-020-00407-2. Mol Neurodegener. 2020. PMID: 33032659 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma levels of soluble TREM2 and neurofilament light chain in TREM2 rare variant carriers.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019 Nov 28;11(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0545-5. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31779670 Free PMC article.
-
Early increase of CSF sTREM2 in Alzheimer's disease is associated with tau related-neurodegeneration but not with amyloid-β pathology.Mol Neurodegener. 2019 Jan 10;14(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0301-5. Mol Neurodegener. 2019. PMID: 30630532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klunemann HH, Ridha BH, Magy L, Wherrett JR, Hemelsoet DM, Keen RW, et al. The genetic causes of basal ganglia calcification, dementia, and bone cysts: DAP12 and TREM2. Neurology. 2005;64(9):1502–1507. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000160304.00003.CA. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

