Risk Related to Pre-Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetes Mellitus in Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: Insights From Prospective Comparison of ARNI With ACEI to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure Trial
- PMID: 26754626
- PMCID: PMC4718182
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.115.002560
Risk Related to Pre-Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetes Mellitus in Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: Insights From Prospective Comparison of ARNI With ACEI to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure Trial
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of pre-diabetes mellitus and its consequences in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction are not known. We investigated these in the Prospective Comparison of ARNI With ACEI to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure (PARADIGM-HF) trial.
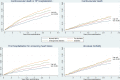
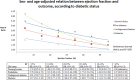
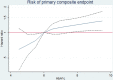
Methods and results: We examined clinical outcomes in 8399 patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction according to history of diabetes mellitus and glycemic status (baseline hemoglobin A1c [HbA1c]: < 6.0% [< 42 mmol/mol], 6.0%-6.4% [42-47 mmol/mol; pre-diabetes mellitus], and ≥ 6.5% [≥ 48 mmol/mol; diabetes mellitus]), in Cox regression models adjusted for known predictors of poor outcome. Patients with a history of diabetes mellitus (n = 2907 [35%]) had a higher risk of the primary composite outcome of heart failure hospitalization or cardiovascular mortality compared with those without a history of diabetes mellitus: adjusted hazard ratio, 1.38; 95% confidence interval, 1.25 to 1.52; P < 0.001. HbA1c measurement showed that an additional 1106 (13% of total) patients had undiagnosed diabetes mellitus and 2103 (25%) had pre-diabetes mellitus. The hazard ratio for patients with undiagnosed diabetes mellitus (HbA1c, > 6.5%) and known diabetes mellitus compared with those with HbA1c < 6.0% was 1.39 (1.17-1.64); P < 0.001 and 1.64 (1.43-1.87); P < 0.001, respectively. Patients with pre-diabetes mellitus were also at higher risk (hazard ratio, 1.27 [1.10-1.47]; P < 0.001) compared with those with HbA1c < 6.0%. The benefit of LCZ696 (sacubitril/valsartan) compared with enalapril was consistent across the range of HbA1c in the trial.
Conclusions: In patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction, dysglycemia is common and pre-diabetes mellitus is associated with a higher risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes (compared with patients with no diabetes mellitus and HbA1c < 6.0%). LCZ696 was beneficial compared with enalapril, irrespective of glycemic status.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT01035255.
Keywords: clinical trial; diabetes mellitus; heart failure; prognosis; treatment outcome.
© 2016 The Authors.
Figures

References
-
- Heidenreich PA, Trogdon JG, Khavjou OA, Butler J, Dracup K, Ezekowitz MD, Finkelstein EA, Hong Y, Johnston SC, Khera A, Lloyd-Jones DM, Nelson SA, Nichol G, Orenstein D, Wilson PW, Woo YJ American Heart Association Advocacy Coordinating Committee; Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; Council on Arteriosclerosis; Thrombosis and Vascular Biology; Council on Cardiopulmonary; Critical Care; Perioperative and Resuscitation; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; Council on the Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, and Interdisciplinary Council on Quality of Care and Outcomes Research. Forecasting the future of cardiovascular disease in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011;123:933–944. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31820a55f5. - PubMed
-
- Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lin JK, Singh GM, Paciorek CJ, Cowan MJ, Farzadfar F, Stevens GA, Lim SS, Riley LM, Ezzati M Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors of Chronic Diseases Collaborating Group (Blood Pressure) National, regional, and global trends in systolic blood pressure since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 786 country-years and 5·4 million participants. Lancet. 2011;377:568–577. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62036-3. - PubMed
-
- McMurray JJ, Gerstein HC, Holman RR, Pfeffer MA. Heart failure: a cardiovascular outcome in diabetes that can no longer be ignored. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2:843–851. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70031-2. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB, Hjortland M, Castelli WP. Role of diabetes in congestive heart failure: the Framingham study. Am J Cardiol. 1974;34:29–34. - PubMed
-
- MacDonald MR, Petrie MC, Varyani F, Ostergren J, Michelson EL, Young JB, Solomon SD, Granger CB, Swedberg K, Yusuf S, Pfeffer MA, McMurray JJ CHARM Investigators. Impact of diabetes on outcomes in patients with low and preserved ejection fraction heart failure: an analysis of the Candesartan in Heart failure: Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and morbidity (CHARM) programme. Eur Heart J. 2008;29:1377–1385. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehn153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

