Radiation-induced miR-208a increases the proliferation and radioresistance by targeting p21 in human lung cancer cells
- PMID: 26754670
- PMCID: PMC4710038
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-016-0285-3
Radiation-induced miR-208a increases the proliferation and radioresistance by targeting p21 in human lung cancer cells
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Radiation-induced miR-208a increases the proliferation and radioresistance by targeting p21 in human lung cancer cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jan 28;35:20. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0299-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26822867 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer has long been the most dangerous malignant tumor among males in both well developed and poorly developed countries. Radiotherapy plays a critical role in the curative management of inoperable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and is also used as a post-surgical treatment in lung cancer patients. Radioresistance is an important factor that limits the efficacy of radiotherapy for NSCLC patients. Increasing evidence suggests that microRNAs (miRNAs) possess diverse cellular regulatory roles in radiation responses.
Methods: In this study, we used miRNA microarray technology to identify serum miRNAs that were differentially expressed before and after radiotherapy in lung cancer patients. We further examined the biological function of miR-208a on cell viability, apoptotic death and cell cycle distribution in human lung cancer cells and explored the probable mechanism.
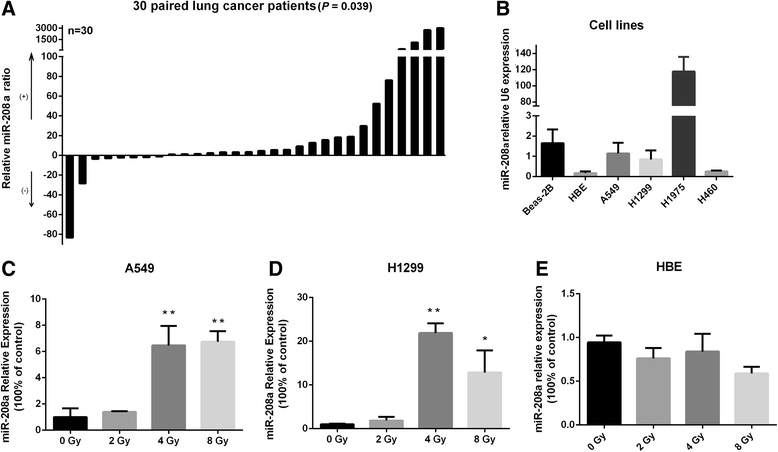
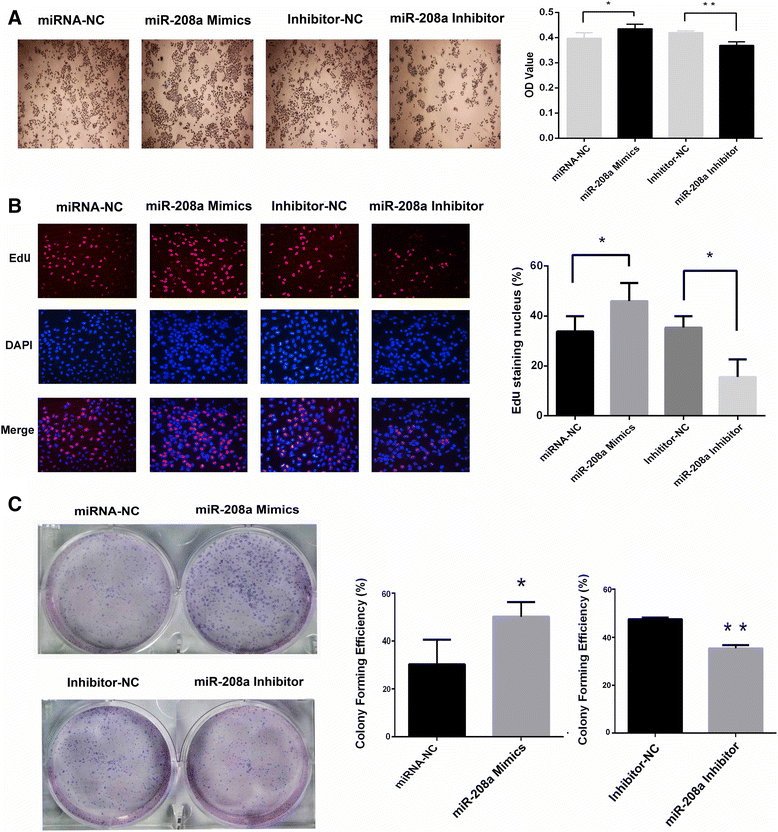
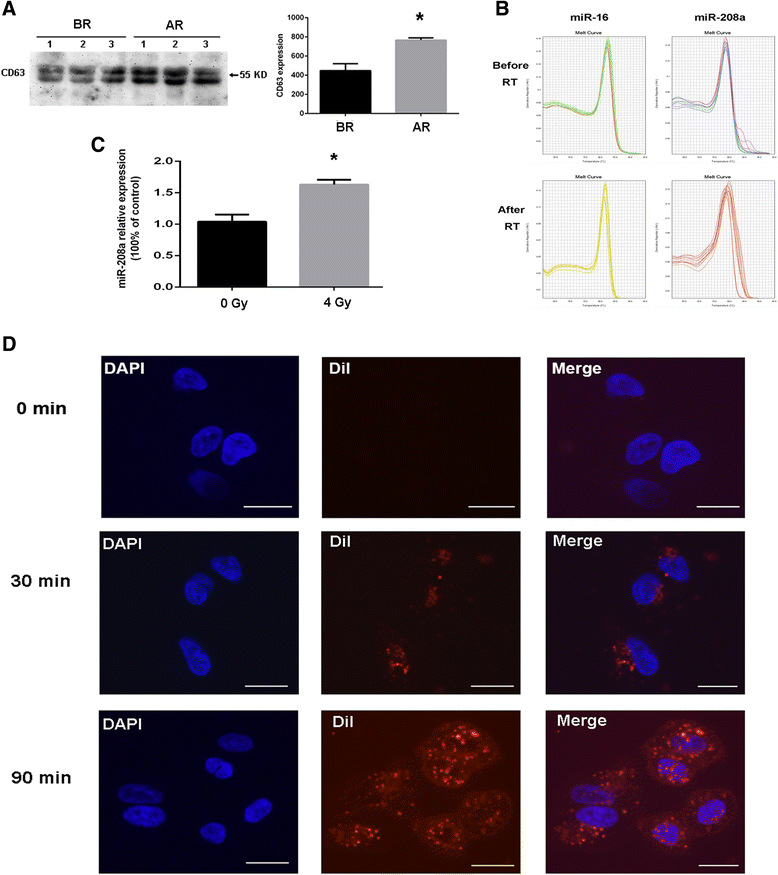
Results: Nine miRNAs, including miR-29b-3p, miR-200a-3p, and miR-126-3p were significantly down-regulated, whereas miR-208a was the only miRNA that was up-regulated in the serum of the patients after radiation treatment (P < 0.05). The expression of miR-208a could be induced by X-ray irradiation in lung cancer cells. Forced expression of miR-208a promoted cell proliferation and induced radioresistance via targeting p21 with a corresponding activation of the AKT/mTOR pathway in lung cancer cells, whereas down-regulation of miR-208a resulted in the opposite effects. In addition, down-regulation of miR-208a increased the percentage of cells undergoing apoptosis and inhibited the G1 phase arrest in NSCLC cells. Moreover, miR-208a from the serum exosome fraction of lung cancer patients could shuttle to A549 cells in a time-dependent manner, which was likely to contribute to the subsequent biological effects.
Conclusions: The present study provides evidence that miR-208a can affect the proliferation and radiosensitivity of human lung cancer cells by targeting p21 and can be transported by exosomes. Thus, miR-208a may serve as a potential therapeutic target for lung cancer patients.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Extracellular miR-1246 promotes lung cancer cell proliferation and enhances radioresistance by directly targeting DR5.Oncotarget. 2016 May 31;7(22):32707-22. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9017. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27129166 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma miRNAs in predicting radiosensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):11927-11936. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5052-8. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27075472 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-106b induces cell radioresistance via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathways and p21 in colorectal cancer.J Transl Med. 2015 Aug 4;13:252. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0592-z. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26238857 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of miRNAs affects radiobiological response of lung cancer stem cells.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:851841. doi: 10.1155/2015/851841. Epub 2015 Mar 1. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25815339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNAs: Potential glioblastoma radiosensitizer by targeting radiation-related molecular pathways.Mutat Res. 2019 Nov;816-818:111679. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2019.111679. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Mutat Res. 2019. PMID: 31715522 Review.
Cited by
-
Polyphenols as Lung Cancer Chemopreventive Agents by Targeting microRNAs.Molecules. 2022 Sep 11;27(18):5903. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185903. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances of exosome isolation techniques in lung cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Sep;47(9):7229-7251. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05715-w. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32789576 Review.
-
miR-122-5p modulates the radiosensitivity of cervical cancer cells by regulating cell division cycle 25A (CDC25A).FEBS Open Bio. 2019 Nov;9(11):1869-1879. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12730. Epub 2019 Sep 29. FEBS Open Bio. 2019. PMID: 31505105 Free PMC article.
-
miR-29b inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression by targeting STRN4.Hum Cell. 2020 Jan;33(1):220-231. doi: 10.1007/s13577-019-00305-w. Epub 2019 Dec 7. Hum Cell. 2020. PMID: 31813135
-
Involvement of Non-Coding RNAs in Chemo- and Radioresistance of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Nov 23;13:8781-8794. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S336265. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34849030 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

