Identification of p62/SQSTM1 as a component of non-canonical Wnt VANGL2-JNK signalling in breast cancer
- PMID: 26754771
- PMCID: PMC4729931
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10318
Identification of p62/SQSTM1 as a component of non-canonical Wnt VANGL2-JNK signalling in breast cancer
Abstract
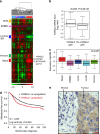
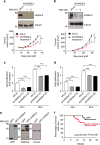
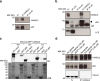
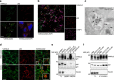
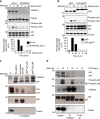
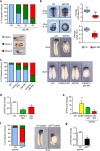
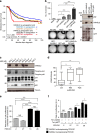
The non-canonical Wnt/planar cell polarity (Wnt/PCP) pathway plays a crucial role in embryonic development. Recent work has linked defects of this pathway to breast cancer aggressiveness and proposed Wnt/PCP signalling as a therapeutic target. Here we show that the archetypal Wnt/PCP protein VANGL2 is overexpressed in basal breast cancers, associated with poor prognosis and implicated in tumour growth. We identify the scaffold p62/SQSTM1 protein as a novel VANGL2-binding partner and show its key role in an evolutionarily conserved VANGL2-p62/SQSTM1-JNK pathway. This proliferative signalling cascade is upregulated in breast cancer patients with shorter survival and can be inactivated in patient-derived xenograft cells by inhibition of the JNK pathway or by disruption of the VANGL2-p62/SQSTM1 interaction. VANGL2-JNK signalling is thus a potential target for breast cancer therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Anastas J. N. & Moon R. T. WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 13, 11–26 (2013) . - PubMed
-
- Bukholm I. K., Nesland J. M., Karesen R., Jacobsen U. & Borresen-Dale A. L. E-cadherin and alpha-, beta-, and gamma-catenin protein expression in relation to metastasis in human breast carcinoma. J. Pathol. 185, 262–266 (1998) . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

