Implicit short- and long-term memory direct our gaze in visual search
- PMID: 26754811
- PMCID: PMC4819550
- DOI: 10.3758/s13414-015-1021-3
Implicit short- and long-term memory direct our gaze in visual search
Abstract
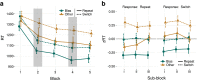
Visual attention is strongly affected by the past: both by recent experience and by long-term regularities in the environment that are encoded in and retrieved from memory. In visual search, intertrial repetition of targets causes speeded response times (short-term priming). Similarly, targets that are presented more often than others may facilitate search, even long after it is no longer present (long-term priming). In this study, we investigate whether such short-term priming and long-term priming depend on dissociable mechanisms. By recording eye movements while participants searched for one of two conjunction targets, we explored at what stages of visual search different forms of priming manifest. We found both long- and short- term priming effects. Long-term priming persisted long after the bias was present, and was again found even in participants who were unaware of a color bias. Short- and long-term priming affected the same stage of the task; both biased eye movements towards targets with the primed color, already starting with the first eye movement. Neither form of priming affected the response phase of a trial, but response repetition did. The results strongly suggest that both long- and short-term memory can implicitly modulate feedforward visual processing.
Keywords: Eye movements; Implicit memory; Long-term memory; Priming; Visual search.
Figures


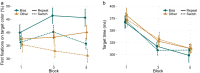


Similar articles
-
The long and the short of priming in visual search.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2015 Jul;77(5):1558-73. doi: 10.3758/s13414-015-0860-2. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2015. PMID: 25832185 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term priming of visual search prevails against the passage of time and counteracting instructions.J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn. 2016 Aug;42(8):1293-303. doi: 10.1037/xlm0000233. Epub 2016 Feb 11. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn. 2016. PMID: 26866654
-
Visual consciousness and intertrial feature priming.J Vis. 2013 Apr 1;13(5):1. doi: 10.1167/13.5.1. J Vis. 2013. PMID: 23547103
-
[Neural Mechanisms of Visual Search and Working Memory].Brain Nerve. 2024 Jun;76(6):709-714. doi: 10.11477/mf.1416202667. Brain Nerve. 2024. PMID: 38853498 Review. Japanese.
-
Neural mechanism of priming in visual search.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2021 Feb;83(2):587-602. doi: 10.3758/s13414-020-02118-8. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2021. PMID: 32914342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Term Visual Memory and Its Role in Learning Suppression.Front Psychol. 2018 Oct 12;9:1896. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01896. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 30369895 Free PMC article.
-
Priming effects in inefficient visual search: Real, but transient.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2022 Jul;84(5):1417-1431. doi: 10.3758/s13414-022-02503-5. Epub 2022 May 16. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2022. PMID: 35578002 Free PMC article.
-
Same, but different: Binding effects in auditory, but not visual detection performance.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2023 Feb;85(2):438-451. doi: 10.3758/s13414-021-02436-5. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2023. PMID: 35107812 Free PMC article.
-
Saccadic landing positions reveal that eye movements are affected by distractor-based retrieval.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2022 Oct;84(7):2219-2235. doi: 10.3758/s13414-022-02538-8. Epub 2022 Aug 17. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2022. PMID: 35978216 Free PMC article.
-
Experiential Knowledge Affects the Visual Search Behaviors of Sprint Coaches and Sport Biomechanists.Front Sports Act Living. 2020 Jul 30;2:95. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2020.00095. eCollection 2020. Front Sports Act Living. 2020. PMID: 33345086 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

