Increasing rate of inflammatory bowel disease: a 12-year retrospective study in NingXia, China
- PMID: 26754840
- PMCID: PMC4710033
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-015-0405-0
Increasing rate of inflammatory bowel disease: a 12-year retrospective study in NingXia, China
Abstract
Background: In China, the incidence of Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has shown a significant growth trend. Analysis of the epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic means, and treatment of IBD will further improve the clinician's understanding of IBD, improve knowledge and further enable early diagnosis and standardized therapeutic management. The purpose of this study was to analyze the clinical characteristics of IBD inpatients in General Hospital of NingXia Medical University over a 12-year period to identify trends in clinical and epidemiological features, clinical manifestations, and treatment programs.
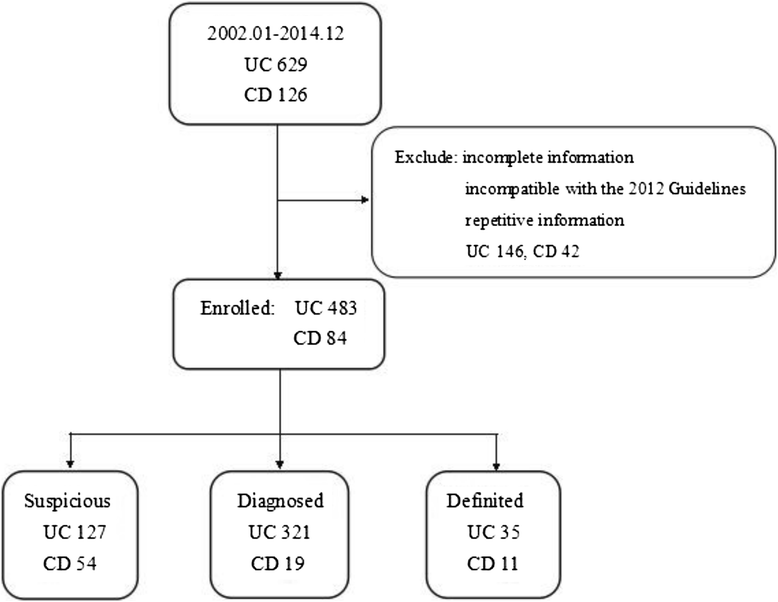
Methods: By excluding188 patients with incomplete information or incompatible with the 2012 Guidlines cases, we retrospectively analyzed the case records of 567 inpatients with a diagnosis of IBD admitted to the General Hospital of NingXia Medical University between January 2002 and December 2014. The clinical epidemiological features, clinical manifestations, diagnostic methods, and therapeutic status were analyzed.
Results: Over the study period, IBD hospitalization rates in 2002 and 2014 groups was 1.96 % and 4.05 %, increased 2.07 times. Of 567 cases of IBD, 483 (85.19 %) cases were categorized as ulcerative colitis (UC) and 84 as Crohn's disease (CD) (14.81 %). Total male cases were 321 (56.61 %). Mean age of cases was 49.06 ± 14.92 years for UC and 44.84 ± 14.67 years for CD. The majority of UC was located in the colon, with a moderate level of disease activity. A combination of clinical manifestations and colonoscopy was mostly used to make a diagnosis; relatively the rate of pathological diagnosis was low, with a small proportion of patient's diagnosed based on radiology. Treatment with SASP/5ASA and steroids was applied to the majority of inpatients and 47.83 % were treated with antibiotics; in contrast, only 1.86 % cases were treated with immunosuppressive therapy.
Conclusions: An increasing trend of admissions for IBD can be observed in our study; there are some differences in clinical features and treatment compared with Western countries, and further research into this is required.
References
-
- Zeng Z, Zhu Z, Yang Y, Ruan W, Peng X, Su Y, et al. Incidence and clinical characteristics of inflammatory bowel disease in a developed region of Guangdong Province, China: a prospective population-based study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28(7):1148–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical