Galectin-3 Is Elevated and Associated With Adverse Outcomes in Patients With Single-Ventricle Fontan Circulation
- PMID: 26755550
- PMCID: PMC4859390
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002706
Galectin-3 Is Elevated and Associated With Adverse Outcomes in Patients With Single-Ventricle Fontan Circulation
Abstract
Background: Galectin-3 may play a role in cardiac and noncardiac fibrosis, and elevated circulating levels of this protein predict adverse outcomes in patients with heart failure who do not have congenital heart disease. We investigated galectin-3 in adults with single-ventricle Fontan circulation, patients who are prone to premature clinical deterioration in the context of extensive multiorgan fibrosis.
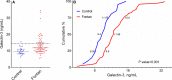
Methods and results: We measured plasma galectin-3 concentrations in 70 ambulatory adult Fontan patients and 21 age- and sex-matched control participants. Galectin-3 level was significantly higher in the Fontan group (11.85 ng/mL, interquartile range 9.9 to 15.0 ng/mL) versus the control group (9.4 ng/mL, interquartile range 8.2 to 10.8 ng/mL; P<0.001). Among Fontan patients, galectin-3 was positively correlated with age, uric acid, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and negatively correlated with estimated glomerular filtration rate. There was no significant relationship between galectin-3 and oxygen saturation, Fontan type, or ventricular morphology. Over a median follow-up of 461 days, 15 events occurred among the Fontan patients: 12 nonelective hospitalizations (with 2 subsequent deaths) and 3 deaths without prior hospitalization. Patients with elevated galectin-3 (n=19, defined as >2 SD above the control group mean value) had a higher risk of nonelective hospitalization or death (hazard ratio 6.0, 95% CI 2.1 to 16.8, P<0.001). This relationship persisted after individual adjustment for covariates including age, New York Heart Association functional class, C-reactive protein, and estimated glomerular filtration rate and after multivariable adjustment for independently predictive covariates (hazard ratio 9.2, 95% CI 2.4 to 35.2, P=0.001).
Conclusions: Galectin-3 concentrations are elevated among adults with a Fontan circulation, and elevated galectin-3 is associated with an increased risk of nonelective cardiovascular hospitalization or death.
Keywords: Fontan procedure; adult congenital heart disease; biomarker; congenital heart disease; galectin‐3.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures


Comment in
-
Biomarkers and the Fontan Circulation.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 Jan 11;5(1):e002926. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002926. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. PMID: 26755551 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ghaferi AA, Hutchins GM. Progression of liver pathology in patients undergoing the Fontan procedure: chronic passive congestion, cardiac cirrhosis, hepatic adenoma, and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;129:1348–1352. - PubMed
-
- Mertens L, Hagler DJ, Sauer U, Somerville J, Gewillig M. Protein‐losing enteropathy after the Fontan operation: an international multicenter study. PLE study group. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1998;115:1063–1073. - PubMed
-
- Paridon SM, Mitchell PD, Colan SD, Williams RV, Blaufox A, Li JS, Margossian R, Mital S, Russell J, Rhodes J. A cross‐sectional study of exercise performance during the first 2 decades of life after the Fontan operation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:99–107. - PubMed
-
- Fontan F, Kirklin JW, Fernandez G, Costa F, Naftel DC, Tritto F, Blackstone EH. Outcome after a “perfect” Fontan operation. Circulation. 1990;81:1520–1536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

