Unique Regulatory Properties of Heterotetrameric Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptors Revealed by Studying Concatenated Receptor Constructs
- PMID: 26755721
- PMCID: PMC4777821
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.705301
Unique Regulatory Properties of Heterotetrameric Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptors Revealed by Studying Concatenated Receptor Constructs
Abstract
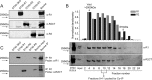
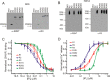
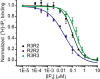
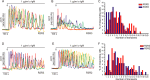
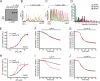
The ability of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (IP3R) to precisely initiate and generate a diverse variety of intracellular Ca(2+) signals is in part mediated by the differential regulation of the three subtypes (R1, R2, and R3) by key functional modulators (IP3, Ca(2+), and ATP). However, the contribution of IP3R heterotetramerization to Ca(2+) signal diversity has largely been unexplored. In this report, we provide the first definitive biochemical evidence of endogenous heterotetramer formation. Additionally, we examine the contribution of individual subtypes within defined concatenated heterotetramers to the shaping of Ca(2+) signals. Under conditions where key regulators of IP3R function are optimal for Ca(2+) release, we demonstrate that individual monomers within heteromeric IP3Rs contributed equally toward generating a distinct 'blended' sensitivity to IP3 that is likely dictated by the unique IP3 binding affinity of the heteromers. However, under suboptimal conditions where [ATP] were varied, we found that one subtype dictated the ATP regulatory properties of heteromers. We show that R2 monomers within a heterotetramer were both necessary and sufficient to dictate the ATP regulatory properties. Finally, the ATP-binding site B in R2 critical for ATP regulation was mutated and rendered non-functional to address questions relating to the stoichiometry of IP3R regulation. Two intact R2 monomers were sufficient to maintain ATP regulation in R2 homotetramers. In summary, we demonstrate that heterotetrameric IP3R do not necessarily behave as the sum of the constituent subunits, and these properties likely extend the versatility of IP3-induced Ca(2+) signaling in cells expressing multiple IP3R isoforms.
Keywords: ATP binding; Concatemer; calcium; calcium channel; calcium intracellular release; inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3); inositol trisphosphate receptor (InsP3R).
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


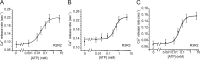



References
-
- Chin K. V., Cade C., Brostrom C. O., Galuska E. M., and Brostrom M. A. (1987) Calcium-dependent regulation of protein synthesis at translational initiation in eukaryotic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 16509–16514 - PubMed
-
- Mattson M. P., and Chan S. L. (2003) Calcium orchestrates apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 5, 1041–1043 - PubMed
-
- Berridge M. J., Lipp P., and Bootman M. D. (2000) The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1, 11–21 - PubMed
-
- Berridge M. J. (1993) Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature 361, 315–325 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

