The emerging role of endothelin-1 in the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia
- PMID: 26755746
- PMCID: PMC5933567
- DOI: 10.1177/1753944715624853
The emerging role of endothelin-1 in the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia
Abstract
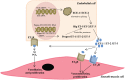
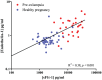
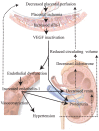
Pre-eclampsia (PE) is the most frequently encountered medical complication during pregnancy. It is characterized by a rise in systemic vascular resistance with a relatively low cardiac output and hypovolemia, combined with severe proteinuria. Despite the hypovolemia, renin-angiotensin system (RAS) activity is suppressed and aldosterone levels are decreased to the same degree as renin. This suggests that the RAS is not the cause of the hypertension in PE, but rather that its suppression is the consequence of the rise in blood pressure. Abnormal placentation early in pregnancy is widely assumed to be an important initial event in the onset of PE. Eventually, this results in the release of anti-angiogenic factors [in particular, soluble Fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1)] and cytokines, leading to generalized vascular dysfunction. Elevated sFlt-1 levels bind and inactivate vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Of interest, VEGF inhibition with drugs like sunitinib, applied in cancer patients, results in a PE-like syndrome, characterized by hypertension, proteinuria and renal toxicity. Both in cancer patients treated with sunitinib and in pregnant women with PE, significant rises in endothelin-1 occur. Multiple regression analysis revealed that endothelin-1 is an independent determinant of the hypertension and proteinuria in PE, and additionally a renin suppressor. Moreover, studies in animal models representative of PE, have shown that endothelin receptor blockers prevent the development of this disease. Similarly, endothelin receptor blockers are protective during sunitinib treatment. Taken together, activation of the endothelin system emerges as an important pathway causing the clinical manifestations of PE. This paper critically addresses this concept, taking into consideration both clinical and preclinical data, and simultaneously discusses the therapeutic consequences of this observation.
Keywords: angiotensin; auto-antibody; cancer; endothelial growth factor; endothelin-1; nitric oxide; pre-eclampsia; soluble Fms-like tyrosine kinase 1; vascular endothelial growth factor.
© The Author(s), 2016.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in pre-eclampsia: the delicate balance between good and bad.Clin Sci (Lond). 2014 Apr;126(8):537-44. doi: 10.1042/CS20130455. Clin Sci (Lond). 2014. PMID: 24400721 Review.
-
Association studies suggest a key role for endothelin-1 in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia and the accompanying renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system suppression.Hypertension. 2015 Jun;65(6):1316-23. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05267. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Hypertension. 2015. PMID: 25870197
-
[Endothelin 1 and angiotensin II in preeeclampsia].Rev Invest Clin. 2007 Jan-Feb;59(1):48-56. Rev Invest Clin. 2007. PMID: 17569300 Review. Spanish.
-
The relationship between circulating endothelin-1, soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 and soluble endoglin in preeclampsia.J Hum Hypertens. 2012 Apr;26(4):236-41. doi: 10.1038/jhh.2011.29. Epub 2011 Mar 31. J Hum Hypertens. 2012. PMID: 21451568
-
Dysregulation of anti-angiogenic agents (sFlt-1, PLGF, and sEndoglin) in preeclampsia--a step forward but not the definitive answer.J Reprod Immunol. 2009 Nov;82(2):106-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2009.09.001. Epub 2009 Oct 23. J Reprod Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19853925 Review.
Cited by
-
The L-NAME mouse model of preeclampsia and impact to long-term maternal cardiovascular health.Life Sci Alliance. 2022 Aug 5;5(12):e202201517. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201517. Life Sci Alliance. 2022. PMID: 36260752 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular biology of uterine fibroids: connecting fibroids and vascular disorders.Reproduction. 2021 Jul 8;162(2):R1-R18. doi: 10.1530/REP-21-0087. Reproduction. 2021. PMID: 34034234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ameliorative effect of apelin-13 against renal complications in L-NAME-induced preeclampsia in rats.PeerJ. 2021 Mar 31;9:e11110. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11110. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33850656 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) -786 T/C and 27-bp VNTR 4b/a Polymorphisms and Preeclampsia Development.Reprod Sci. 2021 Dec;28(12):3529-3539. doi: 10.1007/s43032-021-00632-0. Epub 2021 May 27. Reprod Sci. 2021. PMID: 34046868
-
Endothelial dysfunction in preterm infants: The hidden legacy of uteroplacental pathologies.Front Pediatr. 2022 Nov 4;10:1041919. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.1041919. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36405831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aggarwal P., Chandel N., Jain V., Jha V. (2012) The relationship between circulating endothelin-1, soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 and soluble endoglin in pre-eclampsia. J Hum Hypertens 26: 236–241. - PubMed
-
- Alexander B., Kassab S., Miller M., Abram S., Reckelhoff J., Bennett W., et al. (2001a) Reduced uterine perfusion pressure during pregnancy in the rat is associated with increases in arterial pressure and changes in renal nitric oxide. Hypertension 37: 1191–1195. - PubMed
-
- Alexander B., Rinewalt A., Cockrell K., Massey M., Bennett W., Granger J. (2001b) Endothelin type a receptor blockade attenuates the hypertension in response to chronic reductions in uterine perfusion pressure. Hypertension 37: 485–489. - PubMed
-
- Aydin S., Benian A., Madazli R., Uludag S., Uzun H., Kaya S. (2004) Plasma malondialdehyde, superoxide dismutase, sE-selectin, fibronectin, endothelin-1 and nitric oxide levels in women with pre-eclampsia. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 113: 21–25. - PubMed
-
- Baker P., Kilby M., Broughton Pipkin F. (1992) The effect of angiotensin II on platelet intracellular free calcium concentration in human pregnancy. J Hypertens 10: 55–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

