Naturally derived anti-hepatitis B virus agents and their mechanism of action
- PMID: 26755870
- PMCID: PMC4698485
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.188
Naturally derived anti-hepatitis B virus agents and their mechanism of action
Abstract
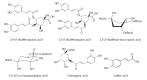
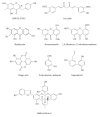
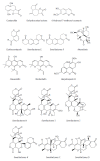
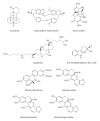
Despite that some approved drugs and genetically engineered vaccines against hepatitis B virus (HBV) are available for HBV patients, HBV infection is still a severe public health problem in the world. All the approved therapeutic drugs (including interferon-alpha and nucleoside analogues) have their limitations. No drugs or therapeutic methods can cure hepatitis B so far. Therefore, it is urgently needed to discover and develop new anti-HBV drugs, especially non-nucleoside agents. Naturally originated compounds with enormous molecular complexity and diversity offer a great opportunity to find novel anti-HBV lead compounds with specific antiviral mechanisms. In this review, the natural products against HBV are discussed according to their chemical classes such as terpenes, lignans, phenolic acids, polyphenols, lactones, alkaloids and flavonoids. Furthermore, novel mode of action or new targets of some representative anti-HBV natural products are also discussed. The aim of this review is to report new discoveries and updates pertaining to anti-HBV natural products in the last 20 years, especially novel skeletons and mode of action. Although many natural products with various skeletons have been reported to exhibit potent anti-HBV effects to date, scarcely any of them are found in the list of conventional anti-HBV drugs worldwide. Additionly, in anti-HBV mechanism of action, only a few references reported new targets or novel mode of action of anti-HBV natural products.
Keywords: Drug target; Hepatitis B virus; Mechanism of action; Natural product; Structure.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Natural Products: Review for Their Effects of Anti-HBV.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Dec 9;2020:3972390. doi: 10.1155/2020/3972390. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33376721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure Properties and Mechanisms of Action of Naturally Originated Phenolic Acids and Their Derivatives against Human Viral Infections.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(38):4279-4302. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170815102917. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28814240 Review.
-
A review of non-nucleoside anti-hepatitis B virus agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2014 Mar 21;75:267-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.01.046. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Eur J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24549242 Review.
-
Naturally occurring and synthetic bioactive molecules as novel non-nucleoside HBV inhibitors.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2010 Feb;10(2):162-71. doi: 10.2174/138955710791185118. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20408799 Review.
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of helioxanthin analogues.Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Apr 1;21(7):2163-76. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.11.037. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23465436
Cited by
-
Plant-derived antiviral drugs as novel hepatitis B virus inhibitors: Cell culture and molecular docking study.Saudi Pharm J. 2019 Mar;27(3):389-400. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2018.12.008. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Saudi Pharm J. 2019. PMID: 30976183 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting phytoprotection in the COVID-19-induced lung damage and associated systemic effects-the evidence-based 3PM proposition to mitigate individual risks.EPMA J. 2021 Aug 3;12(3):325-347. doi: 10.1007/s13167-021-00249-y. eCollection 2021 Sep. EPMA J. 2021. PMID: 34367380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medicinal plants: Treasure for antiviral drug discovery.Phytother Res. 2021 Jul;35(7):3447-3483. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7039. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Phytother Res. 2021. PMID: 33590931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secondary plant metabolites as potent drug candidates against antimicrobial-resistant pathogens.SN Appl Sci. 2022;4(8):209. doi: 10.1007/s42452-022-05084-y. Epub 2022 Jul 8. SN Appl Sci. 2022. PMID: 35821909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The A-Z of Zika drug discovery.Drug Discov Today. 2018 Nov;23(11):1833-1847. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2018.06.014. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Drug Discov Today. 2018. PMID: 29935345 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McMahon BJ. The natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 2009;49:S45–S55. - PubMed
-
- Ott JJ, Stevens GA, Groeger J, Wiersma ST. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection: new estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity. Vaccine. 2012;30:2212–2219. - PubMed
-
- Locarnini S, Hatzakis A, Chen DS, Lok A. Strategies to control hepatitis B: Public policy, epidemiology, vaccine and drugs. J Hepatol. 2015;62:S76–S86. - PubMed
-
- Huang J, Su D, Feng Y, Liu K, Song Y. Antiviral herbs--present and future. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2014;14:61–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

