Differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma from its various mimickers in liver magnetic resonance imaging: What are the tips when using hepatocyte-specific agents?
- PMID: 26755877
- PMCID: PMC4698493
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.284
Differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma from its various mimickers in liver magnetic resonance imaging: What are the tips when using hepatocyte-specific agents?
Abstract
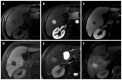
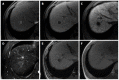
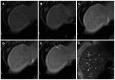
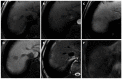
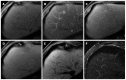
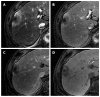
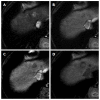
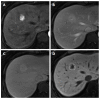
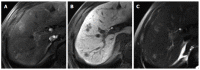
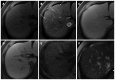
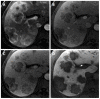
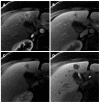
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common primary hepatic malignant tumor. With widespread use of liver imaging, various cirrhosis-related nodules are frequently detected in patients with chronic liver disease, while diverse hypervascular hepatic lesions are incidentally detected but undiagnosed on dynamic computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). However, use of hepatocyte-specific MR contrast agents with combined perfusion and hepatocyte-selective properties have improved diagnostic performance in detection and characterization of focal liver lesions. Meanwhile, the enhancement patterns observed during dynamic phases using hepatocyte-specific agents may be different from those observed during MRI using conventional extracellular fluid agents, leading to confusion in diagnosis. Therefore, we discuss useful tips for the differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma from similar lesions in patients with and without chronic liver disease using liver MRI with hepatocyte-specific agents.
Keywords: Gadoxetic acid; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Liver cirrhosis; Magnetic resonance imaging.
Figures
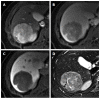
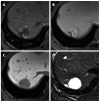
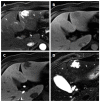
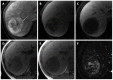
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- European Association For The Study Of The Liver; European Organisation For Research And Treatment Of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56:908–943. - PubMed
-
- Colli A, Fraquelli M, Casazza G, Massironi S, Colucci A, Conte D, Duca P. Accuracy of ultrasonography, spiral CT, magnetic resonance, and alpha-fetoprotein in diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:513–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

