Roles of Periostin in Respiratory Disorders
- PMID: 26756066
- PMCID: PMC4872656
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201510-2032PP
Roles of Periostin in Respiratory Disorders
Abstract
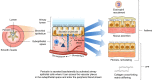
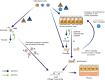
Periostin is a matricellular protein that has been implicated in many disease states. It interacts with multiple signaling cascades to modulate the expression of downstream genes that regulate cellular interactions within the extracellular matrix. This review focuses on the role of periostin in respiratory diseases, including asthma and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, and its potential to help guide treatment or assess prognosis. Epithelial injury is a common feature of many respiratory diseases, resulting in the secretion, among others, of periostin, which is subsequently involved in airway remodeling and other aspects of pulmonary pathophysiology. In asthma, periostin is recognized as a biomarker of type 2 inflammation; POSTN gene expression is up-regulated in bronchial epithelial cells by IL-13 and IL-4. Serum periostin has been evaluated for the identification of patients with increased clinical benefit from treatment with anti-IL-13 (lebrikizumab, tralokinumab) and anti-IgE (omalizumab) therapy and may be prognostic for increased risk of asthma exacerbations and progressive lung function decline. Furthermore, in asthma, periostin may regulate subepithelial fibrosis and mucus production and may serve as a systemic biomarker of eosinophilic airway inflammation. Periostin is also highly expressed in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, and its serum levels may predict clinical progression. Overall, periostin contributes to multiple pathogenic processes across respiratory diseases, and peripheral blood levels of periostin may have utility as a biomarker of treatment response and disease progression.
Keywords: airway remodeling; asthma; biomarker; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; periostin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of periostin in lung fibrosis and airway remodeling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Dec;74(23):4305-4314. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2649-z. Epub 2017 Sep 16. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28918442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of periostin, FENO, IL-13, lebrikzumab, other IL-13 antagonist and dual IL-4/IL-13 antagonist in asthma.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014 Feb;14(2):165-81. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2014.859673. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24283478 Review.
-
Roles of Periostin in Asthma.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1132:145-159. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-6657-4_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31037633 Review.
-
Periostin: a novel component of subepithelial fibrosis of bronchial asthma downstream of IL-4 and IL-13 signals.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006 Jul;118(1):98-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2006.02.046. Epub 2006 Apr 27. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16815144
-
Increased periostin associates with greater airflow limitation in patients receiving inhaled corticosteroids.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Aug;132(2):305-12.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.04.050. Epub 2013 Jun 19. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23791506
Cited by
-
Residual nasal polyp tissue following dupilumab therapy is associated with periostin-associated fibrosis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Apr;281(4):1807-1817. doi: 10.1007/s00405-023-08336-8. Epub 2023 Nov 18. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 37979011
-
Role of periostin in ECRS.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Aug;278(8):2665-2672. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-06369-x. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 32954441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The IL-13-OVOL1-FLG axis in atopic dermatitis.Immunology. 2019 Dec;158(4):281-286. doi: 10.1111/imm.13120. Epub 2019 Oct 1. Immunology. 2019. PMID: 31509236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Interleukin 13 rs20541 Gene Polymorphism and Serum Periostin with Asthma and Allergic Conjunctivitis Among Egyptian Patients.J Asthma Allergy. 2022 Jul 26;15:971-982. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S373098. eCollection 2022. J Asthma Allergy. 2022. PMID: 35923761 Free PMC article.
-
Serum levels of periostin and exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in asthmatic children.World Allergy Organ J. 2019 Jan 26;12(1):100004. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2018.11.004. eCollection 2019. World Allergy Organ J. 2019. PMID: 30937129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Horiuchi K, Amizuka N, Takeshita S, Takamatsu H, Katsuura M, Ozawa H, Toyama Y, Bonewald LF, Kudo A. Identification and characterization of a novel protein, periostin, with restricted expression to periosteum and periodontal ligament and increased expression by transforming growth factor beta. J Bone Miner Res. 1999;14:1239–1249. - PubMed
-
- Liu AY, Zheng H, Ouyang G. Periostin, a multifunctional matricellular protein in inflammatory and tumor microenvironments. Matrix Biol. 2014;37:150–156. - PubMed
-
- Takayama G, Arima K, Kanaji T, Toda S, Tanaka H, Shoji S, McKenzie AN, Nagai H, Hotokebuchi T, Izuhara K. Periostin: a novel component of subepithelial fibrosis of bronchial asthma downstream of IL-4 and IL-13 signals. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;118:98–104. - PubMed
-
- Yuyama N, Davies DE, Akaiwa M, Matsui K, Hamasaki Y, Suminami Y, Yoshida NL, Maeda M, Pandit A, Lordan JL, et al. Analysis of novel disease-related genes in bronchial asthma. Cytokine. 2002;19:287–296. - PubMed
-
- Morra L, Rechsteiner M, Casagrande S, von Teichman A, Schraml P, Moch H, Soltermann A. Characterization of periostin isoform pattern in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2012;76:183–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

