Periprostatic adipocytes act as a driving force for prostate cancer progression in obesity
- PMID: 26756352
- PMCID: PMC4729927
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10230
Periprostatic adipocytes act as a driving force for prostate cancer progression in obesity
Abstract
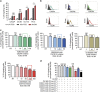
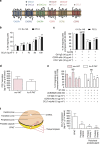
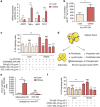
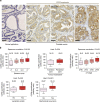
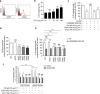
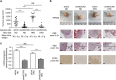
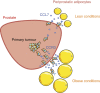
Obesity favours the occurrence of locally disseminated prostate cancer in the periprostatic adipose tissue (PPAT) surrounding the prostate gland. Here we show that adipocytes from PPAT support the directed migration of prostate cancer cells and that this event is strongly promoted by obesity. This process is dependent on the secretion of the chemokine CCL7 by adipocytes, which diffuses from PPAT to the peripheral zone of the prostate, stimulating the migration of CCR3 expressing tumour cells. In obesity, higher secretion of CCL7 by adipocytes facilitates extraprostatic extension. The observed increase in migration associated with obesity is totally abrogated when the CCR3/CCL7 axis is inhibited. In human prostate cancer tumours, expression of the CCR3 receptor is associated with the occurrence of aggressive disease with extended local dissemination and a higher risk of biochemical recurrence, highlighting the potential benefit of CCR3 antagonists in the treatment of prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Part of the authors (VL, AG, BM for Bernard Malavaud, PV and CM) are inventors of a patent application (FR1455491 - PCTIB2015054550) entitled “Inhibition de la chimiokine CCL7 ou de son récepteur CCR3 pour le traitement et le diagnostic du cancer de la prostate”. The remaining authors have no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Prostate cancer: Fat attracts cancer cells.Nat Rev Urol. 2016 Mar;13(3):121. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2016.28. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Nat Rev Urol. 2016. PMID: 26832162 No abstract available.
References
-
- Magi-Galluzzi C. et al. International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Handling and Staging of Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. Working group 3: extraprostatic extension, lymphovascular invasion and locally advanced disease. Mod. Pathol. 24, 26–38 (2011) . - PubMed
-
- Kapoor J. et al. Extraprostatic extension into periprostatic fat is a more important determinant of prostate cancer recurrence than an invasive phenotype. J. Urol. 190, 2061–2066 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Wang Y. Y. et al. Adipose tissue and breast epithelial cells: a dangerous dynamic duo in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 324, 142–151 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

