Histology, Fusion Status, and Outcome in Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma With Low-Risk Clinical Features: A Report From the Children's Oncology Group
- PMID: 26756883
- PMCID: PMC4755849
- DOI: 10.1002/pbc.25862
Histology, Fusion Status, and Outcome in Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma With Low-Risk Clinical Features: A Report From the Children's Oncology Group
Abstract
Background: Distinguishing alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS) from embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) is of prognostic and therapeutic importance. Criteria for classifying these entities evolved significantly from 1995 to 2013. ARMS is associated with inferior outcome; therefore, patients with alveolar histology have generally been excluded from low-risk therapy. However, patients with ARMS and low-risk stage and group (Stage 1, Group I/II/orbit III; or Stage 2/3, Group I/II) were eligible for the Children's Oncology Group (COG) low-risk rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) study D9602 from 1997 to 1999. The characteristics and outcomes of these patients have not been previously reported, and the histology of these cases has not been reviewed using current criteria.
Procedure: We re-reviewed cases that were classified as ARMS on D9602 using current histologic criteria, determined PAX3/PAX7-FOXO1 fusion status, and compared these data with outcome for this unique group of patients.
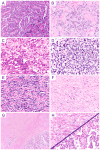
Results: Thirty-eight patients with ARMS were enrolled onto D9602. Only one-third of cases with slides available for re-review (11/33) remained classified as ARMS by current histologic criteria. Most cases were reclassified as ERMS (17/33, 51.5%). Cases that remained classified as ARMS were typically fusion-positive (8/11, 73%), therefore current classification results in a similar rate of fusion-positive ARMS for all clinical risk groups. In conjunction with data from COG intermediate-risk treatment protocol D9803, our data demonstrate excellent outcomes for fusion-negative ARMS with otherwise low-risk clinical features.
Conclusions: Patients with fusion-positive RMS with low-risk clinical features should be classified and treated as intermediate risk, while patients with fusion-negative ARMS could be appropriately treated with reduced intensity therapy.
Keywords: D9602; D9803; alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma; embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma; fusion status; histology; low risk; outcomes; rhabdomyosarcoma.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Newton WA, Jr, Gehan EA, Webber BL, Marsden HB, van Unnik AJ, Hamoudi AB, Tsokos MG, Shimada H, Harms D, Schmidt D, Ninfo V, Cavazzana AO, Gonzalez-Crussi F, Parham DM, Reiman HM, Asmar L, Beltangady MS, Sachs NE, Triche TJ, Maurer HM. Classification of rhabdomyosarcomas and related sarcomas. Pathologic aspects and proposal for a new classification--an Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study. Cancer. 1995;76(6):1073–1085. - PubMed
-
- Barr FG, Smith LM, Lynch JC, Strzelecki D, Parham DM, Qualman SJ, Breitfeld PP. Examination of gene fusion status in archival samples of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma entered on the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study-III trial: a report from the Children's Oncology Group. J Mol Diagn. 2006;8(2):202–208. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sorensen PH, Lynch JC, Qualman SJ, Tirabosco R, Lim JF, Maurer HM, Bridge JA, Crist WM, Triche TJ, Barr FG. PAX3-FKHR and PAX7-FKHR gene fusions are prognostic indicators in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the children's oncology group. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(11):2672–2679. - PubMed
-
- Rudzinski ER, Teot LA, Anderson JR, Moore J, Bridge JA, Barr FG, Gastier-Foster JM, Skapek SX, Hawkins DS, Parham DM. Dense pattern of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, a lesion easily confused with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee of the Children's Oncology Group. Am J Clin Pathol. 2013;140(1):82–90. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Raney RB, Walterhouse DO, Meza JL, Andrassy RJ, Breneman JC, Crist WM, Maurer HM, Meyer WH, Parham DM, Anderson JR. Results of the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group D9602 protocol, using vincristine and dactinomycin with or without cyclophosphamide and radiation therapy, for newly diagnosed patients with low-risk embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee of the Children's Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(10):1312–1318. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

