The CII-specific autoimmune T-cell response develops in the presence of FTY720 but is regulated by enhanced Treg cells that inhibit the development of autoimmune arthritis
- PMID: 26757712
- PMCID: PMC4718028
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-015-0909-6
The CII-specific autoimmune T-cell response develops in the presence of FTY720 but is regulated by enhanced Treg cells that inhibit the development of autoimmune arthritis
Abstract
Background: Fingolimod (FTY720) is an immunomodulating drug that inhibits sphingosine-1-phosphate binding and blocks T-cell egress from lymph nodes. We analyzed the effect of FTY720 on the autoimmune T- and B-cell response in autoimmune arthritis and studied the mechanisms by which it alters the function of T cells.
Methods: Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR1 humanized mice were immunized with type II collagen (CII) and treated with FTY720 three times per week for 3 weeks. Arthritis was evaluated and autoimmune T- and B-cell responses were measured using proliferation assays, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, HLA-DR tetramers, and flow cytometry. The functional capacity of regulatory T (Treg) cells from FTY720-treated mice was measured using an in vitro suppression assay, and the role of Treg cells in inhibiting arthritis in FTY720-treated mice was evaluated using mice treated with anti-CD25 to deplete Treg cells.
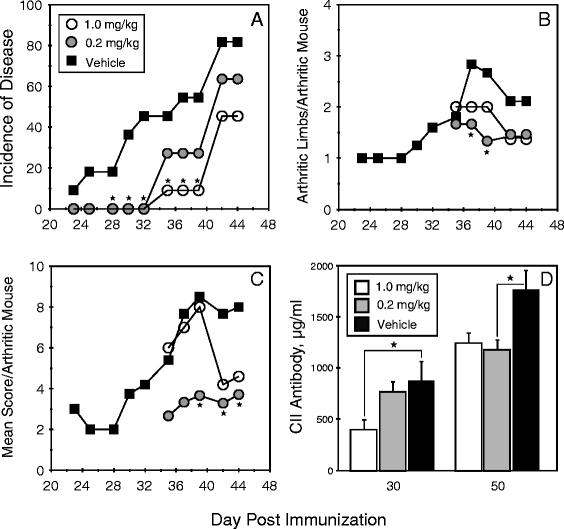
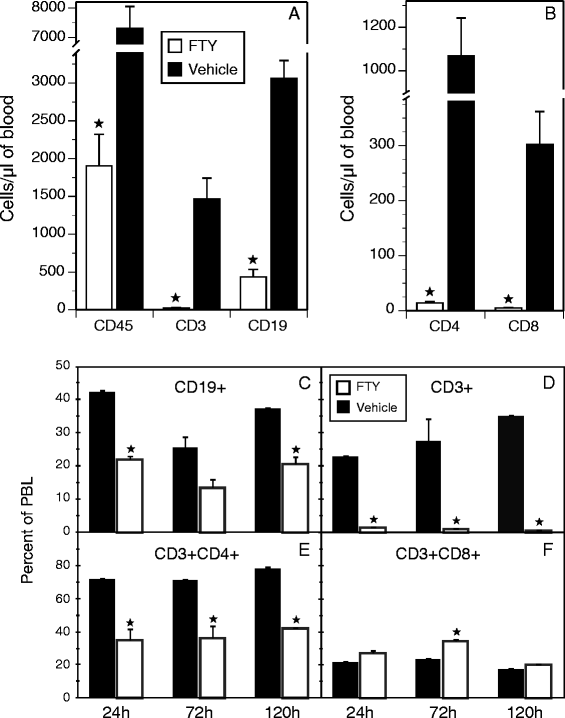
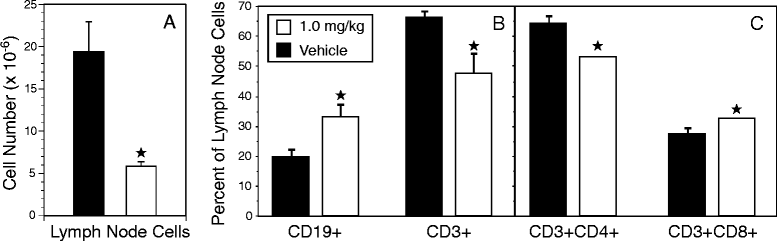
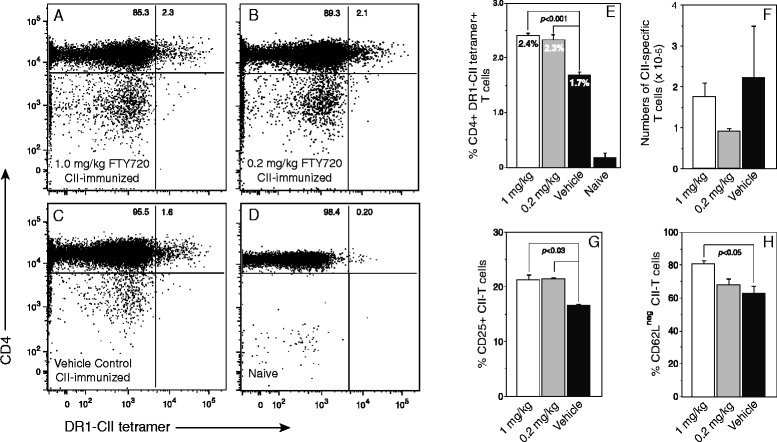
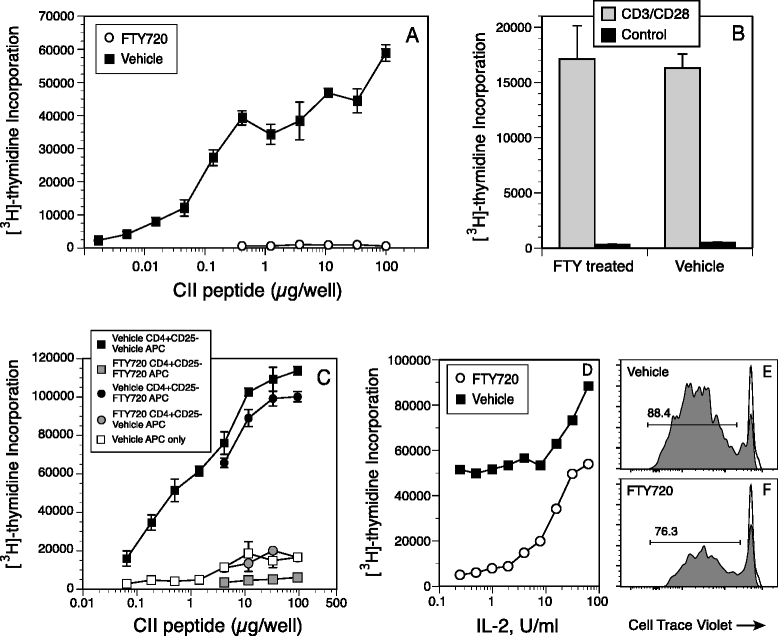
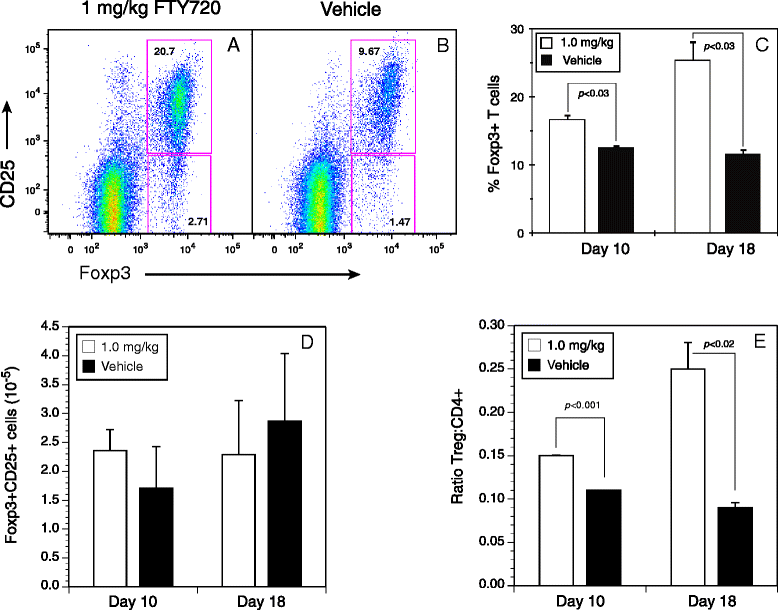
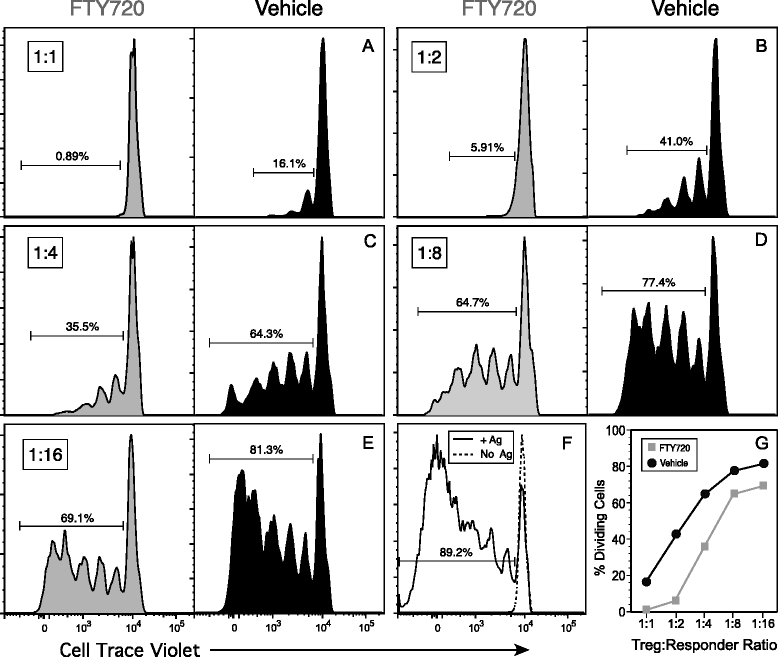
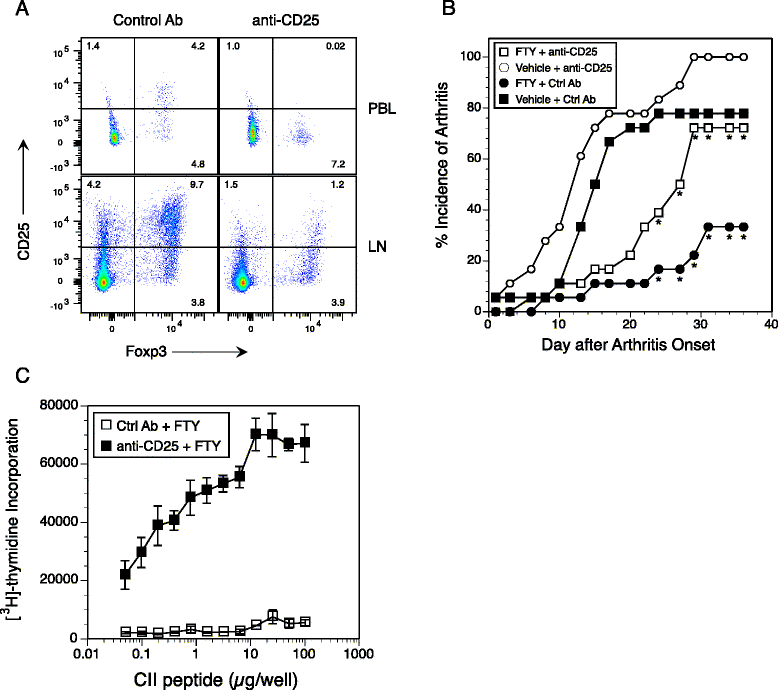
Results: Treatment with FTY720 delayed the onset of arthritis and significantly reduced disease incidence. FTY720 did not prevent the generation of a CII-specific autoimmune T-cell response in vivo. However, as the treatment continued, these T cells became unresponsive to restimulation with antigen in vitro, and this anergic state was reversed by addition of interleukin 2. Measurements of CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) cells in the lymph nodes revealed that the ratio of Treg to helper T (Th) cells increased twofold in the FTY720-treated mice, and in vitro assays indicated that the regulatory function of these cells was enhanced. That FTY720 stimulation of Treg cells played a major role in arthritis inhibition was demonstrated by a loss of disease inhibition and restitution of the T-cell proliferative function after in vivo depletion of the Treg cells.
Conclusions: While FTY720 affects the recirculation of lymphocytes, its ability to inhibit the development of autoimmune arthritis involves several mechanisms, including the enhancement of Treg cell function by increasing the Treg/Th ratio and increased regulatory function on a per-cell basis. FTY720 did not inhibit the development of the autoimmune T-cell response, but disease inhibition appeared to be mediated by Treg cell-mediated suppression of the CII-specific T cells. These data suggest that specific targeting of Treg cells with FTY720 may be a novel therapy for autoimmunity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vasoactive intestinal peptide induces CD4+,CD25+ T regulatory cells with therapeutic effect in collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Mar;54(3):864-76. doi: 10.1002/art.21652. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16508968
-
Evaluation of experimental autoimmune uveitis in mice treated with FTY720.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 May;51(5):2568-74. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4769. Epub 2009 Dec 17. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20019358
-
Involvement of RORγt-overexpressing T cells in the development of autoimmune arthritis in mice.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Apr 20;17(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0606-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25928901 Free PMC article.
-
Immunopathogenesis of collagen arthritis.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2003 Aug;25(1):3-18. doi: 10.1007/s00281-003-0127-1. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2003. PMID: 12904888 Review.
-
Regulatory T cells in experimental autoimmune disease.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2006 Aug;28(1):3-16. doi: 10.1007/s00281-006-0021-8. Epub 2006 Jul 13. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2006. PMID: 16838180 Review.
Cited by
-
Humanized Mouse Models of Rheumatoid Arthritis for Studies on Immunopathogenesis and Preclinical Testing of Cell-Based Therapies.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 19;10:203. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00203. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30837986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-targeted therapeutics in rheumatic diseases.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022 Jun;18(6):335-351. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00784-6. Epub 2022 May 4. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35508810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory T Cell and Forkhead Box Protein 3 as Modulators of Immune Homeostasis.Front Immunol. 2017 May 26;8:605. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00605. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28603524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone loss and aggravated autoimmune arthritis in HLA-DRβ1-bearing humanized mice following oral challenge with Porphyromonas gingivalis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Oct 26;18(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1143-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27784339 Free PMC article.
-
The CXCL10/CXCR3 Axis and Cardiac Inflammation: Implications for Immunotherapy to Treat Infectious and Noninfectious Diseases of the Heart.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:4396368. doi: 10.1155/2016/4396368. Epub 2016 Oct 3. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27795961 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

