Motor imagery training for children with developmental coordination disorder--study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 26758026
- PMCID: PMC4710999
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-016-0530-6
Motor imagery training for children with developmental coordination disorder--study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
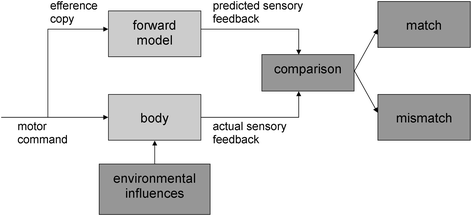
Background: Previous studies have shown that the predictive control of movements is impaired in children with Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD), most likely due to a deficit in the internal modeling of movements. Motor imagery paradigms have been used to test this internal modeling deficit. The aim of the present study is to examine whether a training focused on the mental imagery of motor skills, can help to improve the motor abilities of children with DCD.
Methods/design: A pre-post design will be used to examine the motor performance, motor imagery and motor planning abilities before and after a training of 9 weeks. Two groups will be included in this study (1) one receiving motor imagery (MI) training focused on the forward modeling of purposive actions, (2) one receiving Cognitive Orientation to daily Occupational Performance (CO-OP) training focused on identifying effective cognitive strategies that will increase motor competence. MI training will be given with the use of instruction videos of the motor skill that will be trained. Both groups will participate in 9 individual sessions of 45 min (once a week) with a paediatric physical or occupational therapist, added with homework sessions. Inclusion criteria are: (1) aged 7-12 years, (2) meeting the DSM-V criteria for DCD (motor performance substantially low (score on the m-ABC ≤ 16th percentile) and motor problems that interfere with daily life (DCDQ, and request for help at a paediatric physical or occupational therapist)). Exclusion criteria are IQ < 70 and other medical conditions causing the motor impairment.
Discussion: The results of this study will help to make treatment protocols for children with DCD more evidence-based. This study will increase our knowledge about the efficacy of both the MI training and CO-OP training, and both children with DCD and therapists will benefit from this knowledge.
Trial registration: www.trialregister.nl/NTR5471.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5. Washington: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
-
- Wilson PH, Butson M. Deficits underlying DCD (Chapter 4) In: Geuze RH, editor. Developmental Coordination Disorder: a review of current approaches. Marseille: Solal Editeurs; 2007. pp. 115–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous