EM23, a natural sesquiterpene lactone, targets thioredoxin reductase to activate JNK and cell death pathways in human cervical cancer cells
- PMID: 26758418
- PMCID: PMC4872749
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6828
EM23, a natural sesquiterpene lactone, targets thioredoxin reductase to activate JNK and cell death pathways in human cervical cancer cells
Abstract
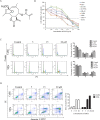
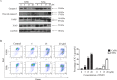
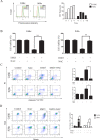
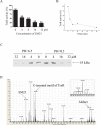
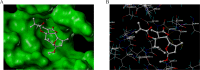
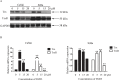
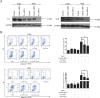
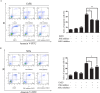
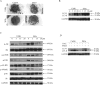
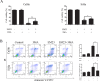
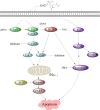
Sesquiterpene lactones (SLs) are the active constituents of a variety of medicinal plants and found to have potential anticancer activities. However, the intracellular molecular targets of SLs and the underlying molecular mechanisms have not been well elucidated. In this study, we observed that EM23, a natural SL, exhibited anti-cancer activity in human cervical cancer cell lines by inducing apoptosis as indicated by caspase 3 activation, XIAP downregulation and mitochondrial dysfunction. Mechanistic studies indicated that EM23-induced apoptosis was mediated by reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the knockdown of thioredoxin (Trx) or thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) resulted in a reduction in apoptosis. EM23 attenuated TrxR activity by alkylation of C-terminal redox-active site Sec498 of TrxR and inhibited the expression levels of Trx/TrxR to facilitate ROS accumulation. Furthermore, inhibition of Trx/TrxR system resulted in the dissociation of ASK1 from Trx and the downstream activation of JNK. Pretreatment with ASK1/JNK inhibitors partially rescued cells from EM23-induced apoptosis. Additionally, EM23 inhibited Akt/mTOR pathway and induced autophagy, which was observed to be proapoptotic and mediated by ROS. Together, these results reveal a potential molecular mechanism for the apoptotic induction observed with SL compound EM23, and emphasize its putative role as a therapeutic agent for human cervical cancer.
Keywords: ROS; apoptosis; sesquiterpene lactone; thioredoxin; thioredoxin reductase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
EM23, A Natural Sesquiterpene Lactone from Elephantopus mollis, Induces Apoptosis in Human Myeloid Leukemia Cells through Thioredoxin- and Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Signaling Pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Mar 29;7:77. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00077. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27064563 Free PMC article.
-
B5, a thioredoxin reductase inhibitor, induces apoptosis in human cervical cancer cells by suppressing the thioredoxin system, disrupting mitochondrion-dependent pathways and triggering autophagy.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 13;6(31):30939-56. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5132. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26439985 Free PMC article.
-
Promotion of HeLa cells apoptosis by cynaropicrin involving inhibition of thioredoxin reductase and induction of oxidative stress.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 May 1;135:216-226. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.03.014. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30880248
-
Thioredoxin system inhibitors as mediators of apoptosis for cancer therapy.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2009 Jan;53(1):87-103. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200700492. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2009. PMID: 18979503 Review.
-
Thioredoxin system in cell death progression.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Dec 15;17(12):1738-47. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4650. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 22530689 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural and Synthetic Lactones Possessing Antitumor Activities.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 21;22(3):1052. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031052. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33494352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Petroleum ether extract of Elephantopus mollis induces senescence and inhibits invasion in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells.3 Biotech. 2025 Feb;15(2):45. doi: 10.1007/s13205-025-04214-8. Epub 2025 Jan 18. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 39834568
-
N-Acetyl-L-cysteine Protects the Enterocyte against Oxidative Damage by Modulation of Mitochondrial Function.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:8364279. doi: 10.1155/2016/8364279. Epub 2016 Nov 27. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 28003713 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Chinese Herbal Medicines in the Treatment of Cervical Cancer.Integr Cancer Ther. 2019 Jan-Dec;18:1534735419861693. doi: 10.1177/1534735419861693. Integr Cancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 31271066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neferine, an alkaloid from lotus seed embryo targets HeLa and SiHa cervical cancer cells via pro-oxidant anticancer mechanism.Phytother Res. 2020 Sep;34(9):2366-2384. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6687. Epub 2020 May 4. Phytother Res. 2020. PMID: 32364634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arner ES. Focus on mammalian thioredoxin reductases—important selenoproteins with versatile functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1790:495–526. - PubMed
-
- Tonissen KF, Di Trapani G. Thioredoxin system inhibitors as mediators of apoptosis for cancer therapy. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2009;53:87–103. - PubMed
-
- Lincoln DT, Ali Emadi EM, Tonissen KF, Clarke FM. The thioredoxin-thioredoxin reductase system: over-expression in human cancer. Anticancer Res. 2003;23:2425–2433. - PubMed
-
- Powis G, Mustacich D, Coon A. The role of the redox protein thioredoxin in cell growth and cancer. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000;29:312–322. - PubMed
-
- Arner ES, Holmgren A. The thioredoxin system in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006;16:420–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

