CD68+ cell count, early evaluation with PET and plasma TARC levels predict response in Hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 26758564
- PMCID: PMC4799945
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.585
CD68+ cell count, early evaluation with PET and plasma TARC levels predict response in Hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
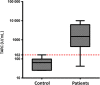
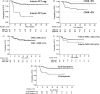
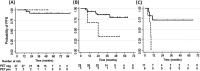
Early response evaluation with [(18) F]fluordeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography after 2 cycles of chemotherapy (interim PET) has been indicated as the strongest predictor for outcome in classical Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). We studied the prognostic role of the number of tumor-infiltrating CD68+ cells and of the plasma levels of TARC (thymus and activation-regulated chemokine) in the context of interim PET in 102 patients with classical HL treated with Adriamycin, Bleomycin, Vinblastine, Dacarbazine (ABVD). After 2 ABVD cycles, interim PET according to Deauville criteria was negative (score 0-3) in 85 patients and positive (score 4-5) in 15 patients (2 patients technically not evaluable). TARC levels were elevated in 89% of patients at diagnosis, and decreased after 2 cycles in 82% of patients. Persistently elevated TARC levels in 18% of patients were significantly associated with a positive PET result (P = 0.007). Strong predictors for progression-free survival (PFS) were a negative interim PET (85% vs. 28%, P < 0.0001) and CD68+ cell counts <5% (89% vs. 67%, P = 0.006), while TARC levels at diagnosis and at interim evaluation had no prognostic role. In multivariate analysis, interim PET, CD68+ cell counts and presence of B-symptoms were independently associated with PFS. We conclude that although TARC levels are a biomarker for early response evaluation, they cannot substitute for interim PET as outcome predictor in HL. The evaluation of CD68 counts and B-symptoms at diagnosis may help to identify low-risk patients regardless positive interim PET.
Keywords: CD68+ tumor-infiltrating macrophages; Hodgkin lymphoma; TARC; interim PET; prognosis.
© 2016 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Townsend, W. , and Linch D.. 2012. Hodgkin's lymphoma in adults. Lancet 380:836–847. - PubMed
-
- Advani, R. 2011. Optimal therapy of advanced Hodgkin lymphoma. Hematology 2011:310–316. - PubMed
-
- Diehl, V. , Franklin J., Pfreundschuh M., Lathan B., Paulus U., Hasenclever D., et al. 2003. Standard and increased‐dose BEACOPP chemotherapy compared with COPP‐ABVD for advanced Hodgkin's disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 348: 2386–2395. - PubMed
-
- Engert, A. , Diehl V., Franklin J., Lohri A., Dörken B., Ludwig W. D., et al. 2009. Escalated‐dose BEACOPP in the treatment of patients with advanced‐stage Hodgkin's lymphoma: 10 years of follow‐up of the GHSG HD9 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 27:4548–4554. - PubMed
-
- Wongso, D. , Fuchs M., Plütschow A., Klimm B., Sasse S., Hertenstein B., et al. 2013. Treatment‐related mortality in patients with advanced‐stage Hodgkin lymphoma: an analysis of the German Hodgkin study group. J. Clin. Oncol. 31:2819–2824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

