Artifacts: The downturn of CBCT image
- PMID: 26759795
- PMCID: PMC4697226
- DOI: 10.4103/2231-0762.170523
Artifacts: The downturn of CBCT image
Abstract
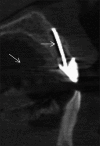
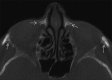
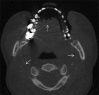
Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) has been accepted as a useful tool for diagnosis and treatment planning in dentistry. Despite a growing trend of CBCT in dentistry, it has some disadvantages like artifacts. Artifacts are discrepancies between the reconstructed visual image and the actual content of the subject which degrade the quality of CBCT images, making them diagnostically unusable. Additionally, structures that do not exist in the subject may appear within images. Such structures can occur because of patient motion, the image capture and reconstruction process. To optimize image quality, it is necessary to understand the types of artifacts. This article aims to throw light on the various types of artifacts associated with CBCT images.
Keywords: Aliasing artifacts; beam hardening; motion artifacts; scanner-related artifacts; stair step artifacts; zebra artifacts.
Figures


References
-
- Ibraheem I. Reduction of artifacts in dental cone beam CT images to improve the three dimensional image reconstruction. J Biomed Sci Eng. 2012;5:409–15.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

