Impact of Hepatitis C Virus on the Circulating Levels of IL-7 in HIV-1 Coinfected Women
- PMID: 26761519
- PMCID: PMC4712709
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000000832
Impact of Hepatitis C Virus on the Circulating Levels of IL-7 in HIV-1 Coinfected Women
Abstract
Objectives: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection causes an alteration in T-cell maturation and activation in patients coinfected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Because interleukin 7 (IL-7) is a major cytokine controlling T-cell homeostasis, we analyzed the potential influence of HCV coinfection on circulating IL-7 levels in HIV-infected women before and after highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART).
Design and methods: This prospective study included 56 HIV monoinfected, 55 HIV/HCV coinfected without HCV viremia, 132 HIV/HCV coinfected with HCV viremia, and 61 HIV/HCV-uninfected women for whom plasma levels of IL-7 were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay at 1 or more follow-up visits before and after HAART. Cross-sectional analyses of the associations between plasma IL-7 levels and HCV infection, demographic, clinical, and immunologic characteristics were evaluated using univariate and multivariate linear regression models before and after HAART.
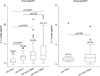
Results: In multivariate models, IL-7 levels were significantly higher in coinfected HCV viremic women than in HIV monoinfected women (multiplicative effect = 1.48; 95% confidence interval: 1.01 to 2.16; P = 0.04) before HAART, but were similar between these two groups among women after HAART. In addition to HCV viremia, higher IL-7 levels were associated with older age (P = 0.02), lower CD4(+) T-cell count (P = 0.0007), and higher natural killer T-cell count (P = 0.02) in women before HAART. Among HAART-treated women, only lower CD4(+) T-cell count was significantly associated with IL-7 level (P = 0.006).
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that in HIV-infected women, circulating levels of IL-7 are strongly associated with CD4 T-cell depletion both before and after HAART. Our data also demonstrate that HCV viremia increases circulating IL-7 levels before HAART but not after HAART in coinfected women. This suggests that the effect of HCV on lymphopenia is abrogated by HAART.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transient liver injury associated with the early recovery of HCV-specific T-cell responses and HCV rebound in HIV-1/HCV coinfected patients undergoing highly active antiretroviral therapy.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2013 Feb 1;62(2):135-42. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3182752d20. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2013. PMID: 23075912
-
Hepatitis C coinfection enhances sensitization of CD4(+) T-cells towards Fas-induced apoptosis in viraemic and HAART-controlled HIV-1-positive patients.Antivir Ther. 2011;16(7):1047-55. doi: 10.3851/IMP1882. Antivir Ther. 2011. PMID: 22024520
-
Evaluating the impact of hepatitis C virus (HCV) on highly active antiretroviral therapy-mediated immune responses in HCV/HIV-coinfected women: role of HCV on expression of primed/memory T cells.J Infect Dis. 2006 May 1;193(9):1202-10. doi: 10.1086/500843. Epub 2006 Mar 17. J Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 16586355 Free PMC article.
-
HIV and hepatitis C coinfection.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008 Jul;23(7 Pt 1):1000-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05489.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 18707597 Review.
-
Early initiation of antiretroviral therapy: the current best way to reduce liver-related deaths in HIV/hepatitis C virus-coinfected patients.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007 Apr 15;44(5):551-6. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31803151c7. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007. PMID: 17224846 Review.
Cited by
-
HCV-coinfection is related to an increased HIV-1 reservoir size in cART-treated HIV patients: a cross-sectional study.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 3;9(1):5606. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41788-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30944340 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Inflammation and Coagulation Biomarkers and Carotid Atherosclerosis Among Treated People With Human Immunodeficiency Virus.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022 Apr 17;9(7):ofac208. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofac208. eCollection 2022 Jul. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35794947 Free PMC article.
-
Diminished plasma levels of common γ-chain cytokines in pulmonary tuberculosis and reversal following treatment.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 27;12(4):e0176495. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176495. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28448542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mackall CL, Fleisher TA, Brown MR, Andrich MP, Chen CC, Feuerstein IM, et al. Distinctions between CD8+ and CD4+ T-cell regenerative pathways result in prolonged T-cell subset imbalance after intensive chemotherapy. Blood. 1997;89:3700–3707. - PubMed
-
- Margolick JB, Munoz A, Donnenberg AD, Park LP, Galai N, Giorgi JV, et al. Failure of T-cell homeostasis preceding AIDS in HIV-1 infection. The Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. Nat Med. 1995;1:674–680. - PubMed
-
- Mastroianni CM, Forcina G, d'Ettorre G, Lichtner M, Mengoni F, D'Agostino C, et al. Circulating levels of interleukin-7 in antiretroviral-naive and highly active antiretroviral therapy-treated HIV-infected patients. HIV Clin Trials. 2001;2:108–112. - PubMed
-
- A. V. HIV and co-infections in people who inject drugs. Geneva: WHO/Department HIV/AIDS; 2012. Available from. http://www.unaids.org/en/media/una.
-
- Anderson KB, Guest JL, Rimland D. Hepatitis C virus coinfection increases mortality in HIV-infected patients in the highly active antiretroviral therapy era: data from the HIV Atlanta VA Cohort Study. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:1507–1513. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UO1-HD-32632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-34994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-34989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI052065/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK041296/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI052065/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-34993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-42590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES025786/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-31834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI052065/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD032632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials