Spatial regulation of greatwall by Cdk1 and PP2A-Tws in the cell cycle
- PMID: 26761639
- PMCID: PMC5056603
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1127476
Spatial regulation of greatwall by Cdk1 and PP2A-Tws in the cell cycle
Abstract
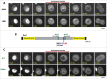
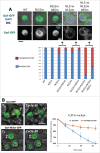
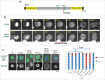
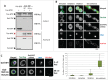
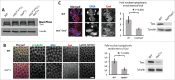
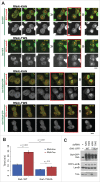
Entry into mitosis requires the phosphorylation of multiple substrates by cyclin B-Cdk1, while exit from mitosis requires their dephosphorylation, which depends largely on the phosphatase PP2A in complex with its B55 regulatory subunit (Tws in Drosophila). At mitotic entry, cyclin B-Cdk1 activates the Greatwall kinase, which phosphorylates Endosulfine proteins, thereby activating their ability to inhibit PP2A-B55 competitively. The inhibition of PP2A-B55 at mitotic entry facilitates the accumulation of phosphorylated Cdk1 substrates. The coordination of these enzymes involves major changes in their localization. In interphase, Gwl is nuclear while PP2A-B55 is cytoplasmic. We recently showed that Gwl suddenly relocalizes from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in prophase, before nuclear envelope breakdown and that this controlled localization of Gwl is required for its function. We and others have shown that phosphorylation of Gwl by cyclin B-Cdk1 at multiple sites is required for its nuclear exclusion, but the precise mechanisms remained unclear. In addition, how Gwl returns to its nuclear localization was not explored. Here we show that cyclin B-Cdk1 directly inactivates a Nuclear Localization Signal in the central region of Gwl. This phosphorylation facilitates the cytoplasmic retention of Gwl, which is exported to the cytoplasm in a Crm1-dependent manner. In addition, we show that PP2A-Tws promotes the return of Gwl to its nuclear localization during cytokinesis. Our results indicate that the cyclic changes in Gwl localization at mitotic entry and exit are directly regulated by the antagonistic cyclin B-Cdk1 and PP2A-Tws enzymes.
Keywords: Cdk1; Cell cycle; Greatwall; Mitosis; PP2A.
Figures
References
-
- Castilho PV, Williams BC, Mochida S, Zhao Y, Goldberg ML. The M phase kinase Greatwall (Gwl) promotes inactivation of PP2A/B55delta, a phosphatase directed against CDK phosphosites. Mol Biol Cell 2009; 20:4777-89; PMID:19793917; http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E09-07-0643 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mayer-Jaekel RE, Ohkura H, Ferrigno P, Andjelkovic N, Shiomi K, Uemura T, Glover DM, Hemmings BA. Drosophila mutants in the 55 kDa regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A show strongly reduced ability to dephosphorylate substrates of p34cdc2. J Cell Sci 1994; 107 ( Pt 9):2609-16; PMID:7844174 - PubMed
-
- Mochida S, Ikeo S, Gannon J, Hunt T. Regulated activity of PP2A-B55 delta is crucial for controlling entry into and exit from mitosis in Xenopus egg extracts. Embo J 2009; 28:2777-85; PMID:19696736; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2009.238 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mochida S, Maslen SL, Skehel M, Hunt T. Greatwall phosphorylates an inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A that is essential for mitosis. Science 2010; 330:1670-3; PMID:21164013; http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1195689 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gharbi-Ayachi A, Labbe JC, Burgess A, Vigneron S, Strub JM, Brioudes E, Van-Dorsselaer A, Castro A, Lorca T. The substrate of Greatwall kinase, Arpp19, controls mitosis by inhibiting protein phosphatase 2A. Science 2010; 330:1673-7; PMID:21164014; http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1197048 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
