Histopathological evaluation of thrombus in patients presenting with stent thrombosis. A multicenter European study: a report of the prevention of late stent thrombosis by an interdisciplinary global European effort consortium
- PMID: 26761950
- PMCID: PMC4872283
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv419
Histopathological evaluation of thrombus in patients presenting with stent thrombosis. A multicenter European study: a report of the prevention of late stent thrombosis by an interdisciplinary global European effort consortium
Abstract
Background: Stent thrombosis (ST) is a rare but serious complication following percutaneous coronary intervention. Analysis of thrombus composition from patients undergoing catheter thrombectomy may provide important insights into the pathological processes leading to thrombus formation. We performed a large-scale multicentre study to evaluate thrombus specimens in patients with ST across Europe.
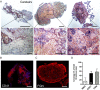
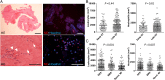
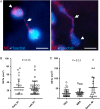
Methods: Patients presenting with ST and undergoing thrombus aspiration were eligible for inclusion. Thrombus collection was performed according to a standardized protocol and specimens were analysed histologically at a core laboratory. Serial tissue cross sections were stained with haematoxylin-eosin (H&E), Carstairs and Luna. Immunohistochemistry was performed to identify leukocyte subsets, prothrombotic neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), erythrocytes, platelets, and fibrinogen.
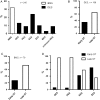
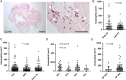
Results: Overall 253 thrombus specimens were analysed; 79 (31.2%) from patients presenting with early ST, 174 (68.8%) from late ST; 79 (31.2%) were from bare metal stents, 166 (65.6%) from drug-eluting stents, 8 (3.2%) were from stents of unknown type. Thrombus specimens displayed heterogeneous morphology with platelet-rich thrombus and fibrin/fibrinogen fragments most abundant; mean platelet coverage was 57% of thrombus area. Leukocyte infiltrations were hallmarks of both early and late ST (early: 2260 ± 1550 per mm(2) vs. late: 2485 ± 1778 per mm(2); P = 0.44); neutrophils represented the most prominent subset (early: 1364 ± 923 per mm(2) vs. late: 1428 ± 1023 per mm(2); P = 0.81). Leukocyte counts were significantly higher compared with a control group of patients with thrombus aspiration in spontaneous myocardial infarction. Neutrophil extracellular traps were observed in 23% of samples. Eosinophils were present in all stent types, with higher numbers in patients with late ST in sirolimus-and everolimus-eluting stents.
Conclusion: In a large-scale study of histological thrombus analysis from patients presenting with ST, thrombus specimens displayed heterogeneous morphology. Recruitment of leukocytes, particularly neutrophils, appears to be a hallmark of ST. The presence of NETs supports their pathophysiological relevance. Eosinophil recruitment suggests an allergic component to the process of ST.
Keywords: Eosinophils; Histopathology; Neutrophil extracellular traps; Neutrophils; Platelets; Stent thrombosis; Thrombus aspiration.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Histopathological thrombus analysis in patients with stent thrombosis: what are the missing pieces in the puzzle?Eur Heart J. 2016 May 14;37(19):1550-2. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw036. Epub 2016 Feb 6. Eur Heart J. 2016. PMID: 26851702 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tada T, Byrne RA, Simunovic I, King LA, Cassese S, Joner M, Fusaro M, Schneider S, Schulz S, Ibrahim T, Ott I, Massberg S, Laugwitz KL, Kastrati A. Risk of stent thrombosis among bare-metal stents, first-generation drug-eluting stents, and second-generation drug-eluting stents: results from a registry of 18,334 patients. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 2013;6:1267–1274. - PubMed
-
- Raber L, Magro M, Stefanini GG, Kalesan B, van Domburg RT, Onuma Y, Wenaweser P, Daemen J, Meier B, Juni P, Serruys PW, Windecker S. Very late coronary stent thrombosis of a newer-generation everolimus-eluting stent compared with early-generation drug-eluting stents: a prospective cohort study. Circulation 2012;125:1110–1121. - PubMed
-
- Schulz S, Schuster T, Mehilli J, Byrne RA, Ellert J, Massberg S, Goedel J, Bruskina O, Ulm K, Schomig A, Kastrati A. Stent thrombosis after drug-eluting stent implantation: incidence, timing, and relation to discontinuation of clopidogrel therapy over a 4-year period. Eur Heart J 2009;30:2714–2721. - PubMed
-
- Windecker S, Kolh P, Alfonso F, Collet JP, Cremer J, Falk V, Filippatos G, Hamm C, Head SJ, Juni P, Kappetein AP, Kastrati A, Knuuti J, Landmesser U, Laufer G, Neumann FJ, Richter DJ, Schauerte P, Sousa Uva M, Stefanini GG, Taggart DP, Torracca L, Valgimigli M, Wijns W, Witkowski A, Authors/Task Force m. 2014 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization: The Task Force on Myocardial Revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS)Developed with the special contribution of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). Eur Heart J 2014;35:2541–2619. - PubMed
-
- Cook S, Ladich E, Nakazawa G, Eshtehardi P, Neidhart M, Vogel R, Togni M, Wenaweser P, Billinger M, Seiler C, Gay S, Meier B, Pichler WJ, Juni P, Virmani R, Windecker S. Correlation of intravascular ultrasound findings with histopathological analysis of thrombus aspirates in patients with very late drug-eluting stent thrombosis. Circulation 2009;120:391–399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

