Alterations of the volatile metabolome in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 26762470
- PMCID: PMC4725859
- DOI: 10.1038/srep19495
Alterations of the volatile metabolome in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
In the present study, we tested whether the volatile metabolome was altered by mutations of the Alzheimer's disease (AD)-implicated amyloid precursor protein gene (APP) and comprehensively examined urinary volatiles that may potentially serve as candidate biomarkers of AD. Establishing additional biomarkers in screening populations for AD will provide enhanced diagnostic specificity and will be critical in evaluating disease-modifying therapies. Having strong evidence of gross changes in the volatile metabolome of one line of APP mice, we utilized three unique mouse lines which over-express human mutations of the APP gene and their respective non-transgenic litter-mates (NTg). Head-space gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) of urinary volatiles uncovered several aberrant chromatographic peak responses. We later employed linear discrimination analysis and found that the GC/MS peak responses provide accurate (>84%) genotype classification of urinary samples. These initial data in animal models show that mutant APP gene expression entails a uniquely identifiable urinary odor, which if uncovered in clinical AD populations, may serve as an additional biomarker for the disease.
Figures
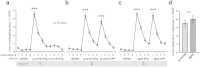
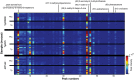
Similar articles
-
Early Candidate Urine Biomarkers for Detecting Alzheimer's Disease Before Amyloid-β Plaque Deposition in an APP (swe)/PSEN1dE9 Transgenic Mouse Model.J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;66(2):613-637. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180412. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 30320578
-
Deciphering metabolic abnormalities associated with Alzheimer's disease in the APP/PS1 mouse model using integrated metabolomic approaches.Biochimie. 2015 Mar;110:119-128. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.01.005. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25597416
-
Metabolomic investigation of systemic manifestations associated with Alzheimer's disease in the APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model.Mol Biosyst. 2015 Sep;11(9):2429-40. doi: 10.1039/c4mb00747f. Mol Biosyst. 2015. PMID: 26131452
-
APP transgenic modeling of Alzheimer's disease: mechanisms of neurodegeneration and aberrant neurogenesis.Brain Struct Funct. 2010 Mar;214(2-3):111-26. doi: 10.1007/s00429-009-0232-6. Epub 2009 Nov 29. Brain Struct Funct. 2010. PMID: 20091183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the function of ABCA7 in Alzheimer's disease.Biochem Soc Trans. 2015 Oct;43(5):920-3. doi: 10.1042/BST20150105. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015. PMID: 26517904 Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in the urine volatile metabolome throughout growth of transplanted hepatocarcinoma.Sci Rep. 2022 May 11;12(1):7774. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11818-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35546342 Free PMC article.
-
The Eye As a Biomarker for Alzheimer's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2016 Nov 17;10:536. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00536. eCollection 2016. Front Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27909396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Symposium: What Does the Microbiome Tell Us about Prevention and Treatment of AD/ADRD?J Neurosci. 2024 Oct 9;44(41):e1295242024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1295-24.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39384409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postnatal Subacute Benzo(a)Pyrene Exposure Caused Neurobehavioral Impairment and Metabolomic Changes of Cerebellum in the Early Adulthood Period of Sprague-Dawley Rats.Neurotox Res. 2018 May;33(4):812-823. doi: 10.1007/s12640-017-9832-8. Epub 2017 Dec 1. Neurotox Res. 2018. PMID: 29197064
-
Urinary metabolic phenotyping for Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 10;10(1):21745. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78031-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33303834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braak H. & Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 82, 239–259 (1991). - PubMed
-
- De Leon M. J. et al. Frequency of hippocampal formation atrophy in normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobio of Aging 18, 1–11 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Frank R. A. et al. Biological markers for therapeutic trials in Alzheimer’s disease: Proceedings of the biological markers working group; NIA initiative on neuroimaging in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobio of Aging 24, 521–536 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

