Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Serum Infliximab Levels During Maintenance Therapy and Outcomes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- PMID: 26763722
- PMCID: PMC4957454
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw007
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Serum Infliximab Levels During Maintenance Therapy and Outcomes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
Background and aims: A number of observational studies have reported an association between serum levels of infliximab [IFX] at various thresholds, and clinical outcomes in inflammatory bowel disease [IBD]. This association has not previously been systematically analysed.
Methods: Systematic review of studies that reported serum infliximab levels according to outcomes in IBD. Primary outcome was clinical remission, and secondary outcomes included endoscopic remission, C-reactive protein [CRP] levels, and colectomy. Meta-analysis of raw data was performed where appropriate. A quality assessment was also undertaken.
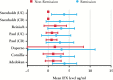
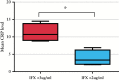
Results: A total of 22 studies met the inclusion criteria, including 3483 patients; 12 studies reported IFX levels in a manner suitable for determining effect estimates. During maintenance therapy, patients in clinical remission had significantly higher mean trough IFX levels than patients not in remission: 3.1 µg/ml versus 0.9 µg/ml. The standardised mean difference in serum IFX levels between groups was 0.6 µg/ml (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.4-0.9, p = 0.0002]. Patients with an IFX level > 2 µg/ml were more likely to be in clinical remission (risk ratio [RR] 2.9, 95% CI 1.8-4.7, p < 0.001], or achieve endoscopic remission [RR 3, 95% CI 1.4-6.5, p = 0.004] than patients with levels < 2 µg/ml.
Conclusions: There is a significant difference between serum infliximab levels in patients with IBD in remission, compared with those who relapse. A trough threshold during maintenance > 2 µg/ml is associated with a greater probability of clinical remission and mucosal healing.
Keywords: Infliximab; mucosal healing; remission; trough.
Copyright © 2016 European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



References
-
- Gisbert JP, Panes J. Loss of response and requirement of infliximab dose intensification in Crohn’s disease: a review. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:760–7. - PubMed
-
- Maser EA, Villela R, Silverberg MS, et al. Association of trough serum infliximab to clinical outcome after scheduled maintenance treatment for Crohn’s disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;4:1248–54. - PubMed
-
- Steenholdt C, Bendtzen K, Brynskov J, et al. Clinical implications of measuring drug and anti-drug antibodies by different assays when optimizing infliximab treatment failure in Crohn’s disease: post hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Am J Gastroenterol 2014;109:1055–64. - PubMed
-
- Adedokun OJ, Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, et al. Association between serum concentration of infliximab and efficacy in adult patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 2014;147:1296–307.e5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

