Coordination of autophagosome-lysosome fusion and transport by a Klp98A-Rab14 complex in Drosophila
- PMID: 26763909
- PMCID: PMC4813314
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.175224
Coordination of autophagosome-lysosome fusion and transport by a Klp98A-Rab14 complex in Drosophila
Abstract
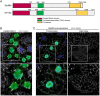
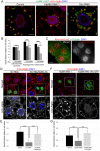
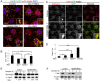
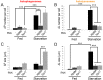
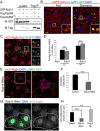
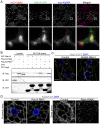
Degradation of cellular material by autophagy is essential for cell survival and homeostasis, and requires intracellular transport of autophagosomes to encounter acidic lysosomes through unknown mechanisms. Here, we identify the PX-domain-containing kinesin Klp98A as a new regulator of autophagosome formation, transport and maturation in Drosophila. Depletion of Klp98A caused abnormal clustering of autophagosomes and lysosomes at the cell center and reduced the formation of starvation-induced autophagic vesicles. Reciprocally, overexpression of Klp98A redistributed autophagic vesicles towards the cell periphery. These effects were accompanied by reduced autophagosome-lysosome fusion and autophagic degradation. In contrast, depletion of the conventional kinesin heavy chain caused a similar mislocalization of autophagosomes without perturbing their fusion with lysosomes, indicating that vesicle fusion and localization are separable and independent events. Klp98A-mediated fusion required the endolysosomal GTPase Rab14, which interacted and colocalized with Klp98A, and required Klp98A for normal localization. Thus, Klp98A coordinates the movement and fusion of autophagic vesicles by regulating their positioning and interaction with the endolysosomal compartment.
Keywords: Autophagy; Intracellular trafficking; Klp98A; Rab14.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Autophagosomes take the Klp98-A train.Small GTPases. 2017 Jan 2;8(1):16-19. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1184776. Epub 2016 May 4. Small GTPases. 2017. PMID: 27142690 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Autophagosomes take the Klp98-A train.Small GTPases. 2017 Jan 2;8(1):16-19. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1184776. Epub 2016 May 4. Small GTPases. 2017. PMID: 27142690 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila Arl8 is a general positive regulator of lysosomal fusion events.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019 Apr;1866(4):533-544. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.12.011. Epub 2018 Dec 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 30590083
-
BORC coordinates encounter and fusion of lysosomes with autophagosomes.Autophagy. 2017 Oct 3;13(10):1648-1663. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1343768. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Autophagy. 2017. PMID: 28825857 Free PMC article.
-
Machinery, regulation and pathophysiological implications of autophagosome maturation.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Nov;22(11):733-750. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00392-4. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34302147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coordination of Autophagosome-Lysosome Fusion by Atg8 Family Members.Curr Biol. 2018 Apr 23;28(8):R512-R518. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.02.034. Curr Biol. 2018. PMID: 29689234 Review.
Cited by
-
The Ubiquitin Receptor ADRM1 Modulates HAP40-Induced Proteasome Activity.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Nov;54(9):7382-7400. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0247-y. Epub 2016 Nov 5. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27815841
-
Exploring Autophagy in Drosophila.Cells. 2017 Jul 12;6(3):22. doi: 10.3390/cells6030022. Cells. 2017. PMID: 28704946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant Compound, Oxyresveratrol, Inhibits APP Production through the AMPK/ULK1/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy Pathway in Mouse Cortical Astrocytes.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Mar 8;10(3):408. doi: 10.3390/antiox10030408. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33800526 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagosomes take the Klp98-A train.Small GTPases. 2017 Jan 2;8(1):16-19. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1184776. Epub 2016 May 4. Small GTPases. 2017. PMID: 27142690 Free PMC article.
-
Rab6 promotes insulin receptor and cathepsin trafficking to regulate autophagy induction and activity in Drosophila.J Cell Sci. 2018 Sep 7;131(17):jcs216127. doi: 10.1242/jcs.216127. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 30111579 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

