Novel Assays for Measurement of Total Cell-Associated HIV-1 DNA and RNA
- PMID: 26763968
- PMCID: PMC4809955
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02904-15
Novel Assays for Measurement of Total Cell-Associated HIV-1 DNA and RNA
Abstract
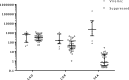
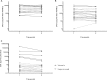
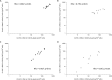
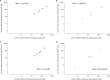
Although a number of PCR-based quantitative assays for measuring HIV-1 persistence during suppressive antiretroviral therapy (ART) have been reported, a simple, sensitive, reproducible method is needed for application to large clinical trials. We developed novel quantitative PCR assays for cell-associated (CA) HIV-1 DNA and RNA, targeting a highly conserved region in HIV-1pol, with sensitivities of 3 to 5 copies/1 million cells. We evaluated the performance characteristics of the assays using peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from 5 viremic patients and 20 patients receiving effective ART. Total and resting CD4(+)T cells were isolated from a subset of patients and tested for comparison with PBMCs. The estimated standard deviations including interassay variability and intra-assay variability of the assays were modest, i.e., 0.15 and 0.10 log10copies/10(6)PBMCs, respectively, for CA HIV-1 DNA and 0.40 and 0.19 log10copies/10(6)PBMCs for CA HIV-1 RNA. Testing of longitudinally obtained PBMC samples showed little variation for either viremic patients (median fold differences of 0.80 and 0.88 for CA HIV-1 DNA and RNA, respectively) or virologically suppressed patients (median fold differences of 1.14 and 0.97, respectively). CA HIV-1 DNA and RNA levels were strongly correlated (r= 0.77 to 1;P= 0.0001 to 0.037) for assays performed using PBMCs from different sources (phlebotomy versus leukapheresis) or using total or resting CD4(+)T cells purified by either bead selection or flow cytometric sorting. Their sensitivity, reproducibility, and broad applicability to small numbers of mononuclear cells make these assays useful for observational and interventional studies that examine longitudinal changes in the numbers of HIV-1-infected cells and their levels of transcription.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of measures of viral reservoirs in HIV-1 eradication studies.PLoS Pathog. 2013 Feb;9(2):e1003174. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003174. Epub 2013 Feb 14. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23459007 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) proviral DNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells by SYBR green real-time PCR technique.J Clin Virol. 2004 Apr;29(4):282-9. doi: 10.1016/S1386-6532(03)00169-0. J Clin Virol. 2004. PMID: 15018857
-
Detection of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus in peripheral blood cells in human immunodeficiency virus infection: association with Kaposi's sarcoma, CD4 cell count, and HIV RNA levels.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1999 Jan 1;15(1):51-5. doi: 10.1089/088922299311709. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1999. PMID: 10024052
-
Viral load in peripheral blood mononuclear cells as surrogate for clinical progression.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995;10 Suppl 2:S51-6. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995. PMID: 7552513 Review.
-
Clinical Relevance of Total HIV DNA in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Compartments as a Biomarker of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders (HAND).Viruses. 2017 Oct 31;9(11):324. doi: 10.3390/v9110324. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 29088095 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NanoHIV: A Bioinformatics Pipeline for Producing Accurate, Near Full-Length HIV Proviral Genomes Sequenced Using the Oxford Nanopore Technology.Cells. 2021 Sep 28;10(10):2577. doi: 10.3390/cells10102577. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685559 Free PMC article.
-
Brief Report: HIV Antibodies Decline During Antiretroviral Therapy but Remain Correlated With HIV DNA and HIV-Specific T-Cell Responses.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2019 Aug 15;81(5):594-599. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002080. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2019. PMID: 31045647 Free PMC article.
-
The largest HIV-1-infected T cell clones in children on long-term combination antiretroviral therapy contain solo LTRs.mBio. 2023 Aug 31;14(4):e0111623. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01116-23. Epub 2023 Aug 2. mBio. 2023. PMID: 37530525 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term persistence of transcriptionally active 'defective' HIV-1 proviruses: implications for persistent immune activation during antiretroviral therapy.AIDS. 2023 Nov 15;37(14):2119-2130. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000003667. Epub 2023 Aug 22. AIDS. 2023. PMID: 37555786 Free PMC article.
-
A Phase 1/2 Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Romidespin in Persons With HIV-1 on Suppressive Antiretroviral Therapy.J Infect Dis. 2021 Aug 16;224(4):648-656. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa777. J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34398236 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Finzi D, Hermankova M, Pierson T, Carruth LM, Buck C, Chaisson RE, Quinn TC, Chadwick K, Margolick J, Brookmeyer R, Gallant J, Markowitz M, Ho DD, Richman DD, Siliciano RF. 1997. Identification of a reservoir for HIV-1 in patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy. Science 278:1295–1300. doi:10.1126/science.278.5341.1295. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Passaes CP, Sáez-Cirión A. 2014. HIV cure research: advances and prospects. Virology 454–455:340–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

