Associations of human retinal very long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids with dietary lipid biomarkers
- PMID: 26764040
- PMCID: PMC4766999
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.P065540
Associations of human retinal very long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids with dietary lipid biomarkers
Abstract
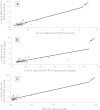
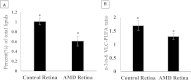
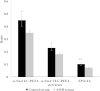
The human retina is well-known to have unique lipid profiles enriched in long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC-PUFAs) and very long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (VLC-PUFAs) that appear to promote normal retinal structure and function, but the influence of diet on retinal lipid profiles in health and disease remains controversial. In this study, we examined two independent cohorts of donor eyes and related their retinal lipid profiles with systemic biomarkers of lipid intake. We found that serum and red blood cell lipids, and to a lesser extent orbital fat, are indeed excellent biomarkers of retinal lipid content and n-3/n-6 ratios in both the LC-PUFA and VLC-PUFA series. Eyes from age-related macular degeneration (AMD) donors have significantly decreased levels of VLC-PUFAs and low n-3/n-6 ratios. These results are consistent with the protective role of dietary n-3 LC-PUFAs against AMD and emphasize the importance of monitoring systemic biomarkers of lipid intake when undertaking clinical trials of lipid supplements for prevention and treatment of retinal disease.
Keywords: age-related macular degeneration; diet and dietary lipids; elongation of very long-chain fatty acids elongase 4; eye; mass spectrometry; nutrition; omega-3 fatty acids; retina.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Fliesler A. J., and Anderson R. E.. 1983. Chemistry and metabolism of lipids in the vertebrate retina. Prog. Lipid Res. 22: 79–131. - PubMed
-
- Aveldaño M. I. 1987. A novel group of very long chain polyenoic fatty acids in dipolyunsaturated phosphatidylcholines from vertebrate retina. J. Biol. Chem. 262: 1172–1179. - PubMed
-
- Suh M., Wierzbicki A. A., Lien E. L., and Clandinin M. T.. 2000. Dietary 20:4n-6 and 22:6n-3 modulates the profile of long- and very-long-chain fatty acids, rhodopsin content, and kinetics in developing photoreceptor cells. Pediatr. Res. 48: 524–530. - PubMed
-
- McMahon A., and Kedzierski W.. 2010. Polyunsaturated very-long-chain C28–C36 fatty acids and retinal physiology. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 94: 1127–1132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

