Lifestyle Changes in Young Adulthood and Middle Age and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality: The Doetinchem Cohort Study
- PMID: 26764411
- PMCID: PMC4859361
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002432
Lifestyle Changes in Young Adulthood and Middle Age and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality: The Doetinchem Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: The associations between overall lifestyle profile and cardiovascular disease (CVD) and death have been mainly investigated in cross-sectional studies. The full benefits of a healthy lifestyle may therefore be underestimated, and the magnitude of benefits associated with changes in lifestyle remains unclear. We quantified the association of changes in lifestyle profiles over 5 years with risk of CVD and all-cause mortality.
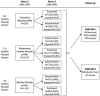
Methods and results: Lifestyle factors (ie, diet, physical activity, smoking, alcohol consumption) and body mass index were assessed and dichotomized as healthy/unhealthy among 5263 adults ages 26 to 66 in 1993-1997 and 5 years later (1998-2002). Multivariable-adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated to quantify associations of change in lifestyle with fatal/nonfatal CVD and all-cause mortality that occurred 8 to 15 years after 1998-2002. Independent of baseline lifestyles, each decrement in number of healthy lifestyle factors was, on average, associated with 35% higher risk of CVD (HR, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.12-1.63) and 37% higher risk of all-cause mortality (HR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.10-1.70); no association was noted with increase in the number of healthy lifestyle factors (P>0.5). Individuals who maintained 4 to 5 healthy lifestyle factors had 2.5 times lower risk of CVD (HR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.25-0.63) and all-cause mortality (HR, 0.40; 95% CI, 0.22-0.73) than those who maintained only 0 to 1 healthy lifestyle factor.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that the benefits of healthy lifestyles may be easier lost than gained over a 5-year period. This underscores the need for efforts to promote maintenance of healthy lifestyles throughout the life course.
Keywords: all‐cause death; cardiovascular disease; lifestyle.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures

References
-
- Eguchi E, Iso H, Tanabe N, Wada Y, Yatsuya H, Kikuchi S, Inaba Y, Tamakoshi A. Healthy lifestyle behaviours and cardiovascular mortality among Japanese men and women: the Japan collaborative cohort study. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:467–477. - PubMed
-
- Ford ES, Bergmann MM, Kroger J, Schienkiewitz A, Weikert C, Boeing H. Healthy living is the best revenge: findings from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition‐Potsdam study. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169:1355–1362. - PubMed
-
- Hoevenaar‐Blom MP, Spijkerman AM, Kromhout D, Verschuren WM. Sufficient sleep duration contributes to lower cardiovascular disease risk in addition to four traditional lifestyle factors: the MORGEN study. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2014;21:1367–1375. - PubMed
-
- Kurth T, Moore SC, Gaziano JM, Kase CS, Stampfer MJ, Berger K, Buring JE. Healthy lifestyle and the risk of stroke in women. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1403–1409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

