Intravenous Versus Oral Iron for the Treatment of Anemia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 26765407
- PMCID: PMC4718233
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002308
Intravenous Versus Oral Iron for the Treatment of Anemia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
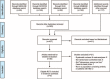
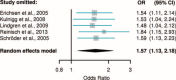
Anemia is the most prevalent extraintestinal complication of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Our aim was to evaluate the comparative efficacy and harm of intravenous (IV) versus oral iron supplementation for correcting anemia in adult IBD patients.We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to integrate evidence from randomized controlled trials having enrolled adults with IBD, and comparing IV versus oral iron (head-to-head) for correcting iron-deficiency anemia. Medline, Embase, Scopus, and the Web of Science database were searched through July 2015. The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, the ClinicalTrials.gov, and international conference proceedings were also investigated. Two reviewers independently abstracted study data and outcomes, and rated each trial's risk-of-bias. Pooled odds ratio (OR) estimates with their 95% CIs were calculated using fixed- and random-effects models.Five eligible studies, including 694 IBD patients, were identified. In meta-analysis, IV iron demonstrated a higher efficacy in achieving a hemoglobin rise of ≥2.0 g/dL as compared to oral iron (OR: 1.57, 95% CI: 1.13, 2.18). Treatment discontinuation rates, due to adverse events or intolerance, were lower in the IV iron groups (OR: 0.27, 95% CI: 0.13, 0.59). Similarly, the occurrence of gastrointestinal adverse events was consistently lower in the IV iron groups. On the contrary, serious adverse events (SAEs) were more frequently reported among patients receiving IV iron preparations (OR: 4.57, 95% CI: 1.11, 18.8); however, the majority of the reported SAEs were judged as unrelated or unlikely to be related to the study medication. We found no evidence of publication bias, or between-study heterogeneity, across all analyses. Risk of bias was high across primary studies, because patients and personnel were not blinded to the intervention.IV iron appears to be more effective and better tolerated than oral iron for the treatment of IBD-associated anemia.
Conflict of interest statement
All other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



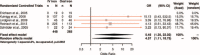
References
-
- Fiorino G, Allocca M, Danese S. Commentary: anaemia in inflammatory bowel disease—the most common and ignored extra intestinal manifestation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2014; 39:227–228. - PubMed
-
- Fiorino G, Allocca M, Danese S. Anemia in inflammatory bowel disease: the opening of Pandora's box? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015; 13:1767–1769. - PubMed
-
- Bager P, Befrits R, Wikman O, et al. High burden of iron deficiency and different types of anemia in inflammatory bowel disease outpatients in Scandinavia: a longitudinal 2-year follow-up study. Scand J Gastroenterol 2013; 48:1286–1293. - PubMed
-
- Gisbert JP, Gomollón F. Common misconceptions in the diagnosis and management of anemia in inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2008; 103:1299–1307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

