Mutation Detection in Patients with Retinal Dystrophies Using Targeted Next Generation Sequencing
- PMID: 26766544
- PMCID: PMC4713063
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145951
Mutation Detection in Patients with Retinal Dystrophies Using Targeted Next Generation Sequencing
Abstract
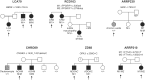
Retinal dystrophies (RD) constitute a group of blinding diseases that are characterized by clinical variability and pronounced genetic heterogeneity. The different nonsyndromic and syndromic forms of RD can be attributed to mutations in more than 200 genes. Consequently, next generation sequencing (NGS) technologies are among the most promising approaches to identify mutations in RD. We screened a large cohort of patients comprising 89 independent cases and families with various subforms of RD applying different NGS platforms. While mutation screening in 50 cases was performed using a RD gene capture panel, 47 cases were analyzed using whole exome sequencing. One family was analyzed using whole genome sequencing. A detection rate of 61% was achieved including mutations in 34 known and two novel RD genes. A total of 69 distinct mutations were identified, including 39 novel mutations. Notably, genetic findings in several families were not consistent with the initial clinical diagnosis. Clinical reassessment resulted in refinement of the clinical diagnosis in some of these families and confirmed the broad clinical spectrum associated with mutations in RD genes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

