High-dose nimotuzumab improves the survival rate of esophageal cancer patients who underwent radiotherapy
- PMID: 26766917
- PMCID: PMC4699509
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S89592
High-dose nimotuzumab improves the survival rate of esophageal cancer patients who underwent radiotherapy
Abstract
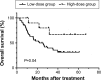
Nimotuzumab (h-R3) is a humanized monoclonal antibody that is safe to use against epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). However, the available information is insufficient about the dose effect of monoclonal antibody against epidermal growth factor receptor for the treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). We retrospectively recruited 66 patients with ESCC who were treated with h-R3 and chemoradiotherapy/radiotherapy. Patients who received more than 1,200 mg of h-R3 were classified as the high-dose group, and the remaining patients were classified as the low-dose group. The endpoint for efficacy was the overall survival. Differences in survival between the groups were analyzed using the log-rank test. The Cox proportional hazards model was used in multivariate analysis to identify independent prognostic factors. The low-dose and high-dose groups comprised 55 and eleven patients, respectively. The median follow-up time in the final analysis was 46 months. The high-dose group showed no increased incidence of toxicities compared to the low-dose group. The 1-, 2-, and 5-year overall survival rates in the low-dose and high-dose groups were 66.9%, 50.0%, 31.5% and 90.0%, 80.0%, 66.7%, respectively (P=0.04). Multivariate analyses showed that the high-dose group had better survival than the low-dose group (hazard ratio 0.28, 95% confidence interval 0.09-0.94, P=0.039). Taken together, high-dose h-R3 showed limited toxicity and improved survival in patients with ESCC.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; monoclonal antibody; nimotuzumab.
Figures
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP, et al. Perioperative chemotherapy versus surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(1):11–20. - PubMed
-
- van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ, et al. Preoperative chemo-radiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(22):2074–2084. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto Y, Yamai H, Seike J, et al. Prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in patients positive for human epidermal growth factor receptor family can be improved by initial chemotherapy with docetaxel, fluorouracil, and cisplatin. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19(3):757–765. - PubMed
-
- Hanawa M, Suzuki S, Dobashi Y, et al. EGFR protein overexpression and gene amplification in squamous cell carcinomas of the esophagus. Int J Cancer. 2006;118(5):1173–1180. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous